Discitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Discitis | |||
| image = [[File:Discitis.jpg]] | |||
| caption = MRI showing discitis at the L4-L5 level | |||
| field = [[Orthopedics]], [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Back pain]], [[fever]], [[neurological deficits]] | |||
| complications = [[Spinal abscess]], [[sepsis]], [[paralysis]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Weeks to months | |||
| causes = [[Bacterial infection]], [[viral infection]] | |||
| risks = [[Immunosuppression]], [[spinal surgery]], [[intravenous drug use]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[blood culture]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Vertebral osteomyelitis]], [[epidural abscess]], [[herniated disc]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antibiotics]], [[pain management]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on early diagnosis and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Pinfecteddisc.png|File:Pinfected disc|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Discitis''' is an [[infection]] or [[inflammation]] of the [[intervertebral disc]] space that affects different age groups. It is a relatively rare condition, which can lead to severe [[pain]] and other complications if not treated promptly. | '''Discitis''' is an [[infection]] or [[inflammation]] of the [[intervertebral disc]] space that affects different age groups. It is a relatively rare condition, which can lead to severe [[pain]] and other complications if not treated promptly. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Discitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including [[bacterial infection]], [[viral infection]], and [[autoimmune disease]]. The most common cause is bacterial infection, often following a [[surgery]] or [[injury]] to the disc space. The bacteria can enter the disc space through the bloodstream or from a nearby infection. | Discitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including [[bacterial infection]], [[viral infection]], and [[autoimmune disease]]. The most common cause is bacterial infection, often following a [[surgery]] or [[injury]] to the disc space. The bacteria can enter the disc space through the bloodstream or from a nearby infection. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The most common symptom of discitis is severe pain in the affected area. The pain is often worse when the patient is moving or putting pressure on the spine. Other symptoms can include [[fever]], [[chills]], and general discomfort or malaise. | The most common symptom of discitis is severe pain in the affected area. The pain is often worse when the patient is moving or putting pressure on the spine. Other symptoms can include [[fever]], [[chills]], and general discomfort or malaise. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of discitis is often challenging due to its rare occurrence and non-specific symptoms. It typically involves a combination of [[medical history]], physical examination, and imaging tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]]. In some cases, a [[biopsy]] of the disc space may be required to confirm the diagnosis. | Diagnosis of discitis is often challenging due to its rare occurrence and non-specific symptoms. It typically involves a combination of [[medical history]], physical examination, and imaging tests such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]]. In some cases, a [[biopsy]] of the disc space may be required to confirm the diagnosis. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for discitis typically involves [[antibiotics]] to treat the infection, along with [[pain management]] to relieve the symptoms. In severe cases, [[surgery]] may be required to remove the infected disc and stabilize the spine. | Treatment for discitis typically involves [[antibiotics]] to treat the infection, along with [[pain management]] to relieve the symptoms. In severe cases, [[surgery]] may be required to remove the infected disc and stabilize the spine. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
With prompt and appropriate treatment, most patients with discitis can recover fully. However, if left untreated, discitis can lead to serious complications such as [[spinal abscess]], [[bone infection]], and [[spinal deformity]]. | With prompt and appropriate treatment, most patients with discitis can recover fully. However, if left untreated, discitis can lead to serious complications such as [[spinal abscess]], [[bone infection]], and [[spinal deformity]]. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Spinal infection]] | * [[Spinal infection]] | ||
* [[Osteomyelitis]] | * [[Osteomyelitis]] | ||
* [[Spondylitis]] | * [[Spondylitis]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Infections]] | [[Category:Infections]] | ||
[[Category:Inflammation]] | [[Category:Inflammation]] | ||
[[Category:Spinal disorders]] | [[Category:Spinal disorders]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Discitis | |
|---|---|
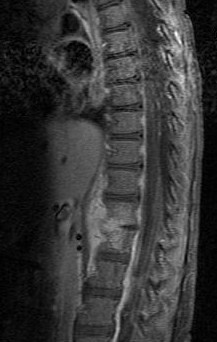
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Back pain, fever, neurological deficits |
| Complications | Spinal abscess, sepsis, paralysis |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Weeks to months |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Bacterial infection, viral infection |
| Risks | Immunosuppression, spinal surgery, intravenous drug use |
| Diagnosis | MRI, blood culture, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Vertebral osteomyelitis, epidural abscess, herniated disc |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, pain management, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on early diagnosis and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Discitis is an infection or inflammation of the intervertebral disc space that affects different age groups. It is a relatively rare condition, which can lead to severe pain and other complications if not treated promptly.
Causes
Discitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial infection, viral infection, and autoimmune disease. The most common cause is bacterial infection, often following a surgery or injury to the disc space. The bacteria can enter the disc space through the bloodstream or from a nearby infection.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of discitis is severe pain in the affected area. The pain is often worse when the patient is moving or putting pressure on the spine. Other symptoms can include fever, chills, and general discomfort or malaise.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of discitis is often challenging due to its rare occurrence and non-specific symptoms. It typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan. In some cases, a biopsy of the disc space may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for discitis typically involves antibiotics to treat the infection, along with pain management to relieve the symptoms. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the infected disc and stabilize the spine.
Prognosis
With prompt and appropriate treatment, most patients with discitis can recover fully. However, if left untreated, discitis can lead to serious complications such as spinal abscess, bone infection, and spinal deformity.


