Central nervous system cyst: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Central nervous system cyst | |||
| image = [[File:Arachnoid_cyst.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = MRI image showing an [[arachnoid cyst]] in the [[central nervous system]] | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[seizures]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[balance disorder]], [[vision problems]] | |||
| complications = [[Hydrocephalus]], [[brain herniation]] | |||
| onset = Varies, can be [[congenital]] or [[acquired]] | |||
| duration = Can be [[chronic (medicine)|chronic]] | |||
| types = [[Arachnoid cyst]], [[colloid cyst]], [[dermoid cyst]], [[epidermoid cyst]] | |||
| causes = [[Developmental anomaly]], [[trauma]], [[infection]], [[tumor]] | |||
| risks = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[head injury]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], [[computed tomography|CT scan]] | |||
| differential = [[Brain tumor]], [[abscess]], [[hematoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical intervention]], [[endoscopic fenestration]], [[shunt (medical)|shunt placement]] | |||
| medication = [[Anticonvulsant]], [[analgesic]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = Rare, usually due to complications | |||
}} | |||
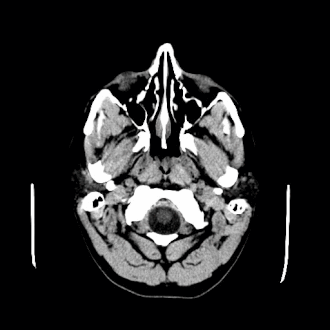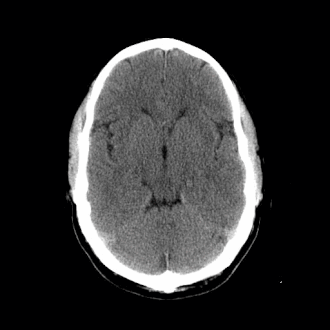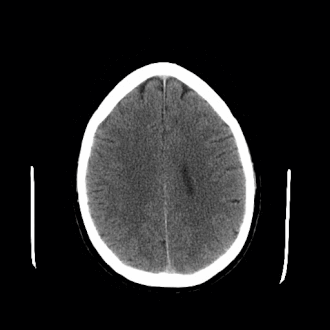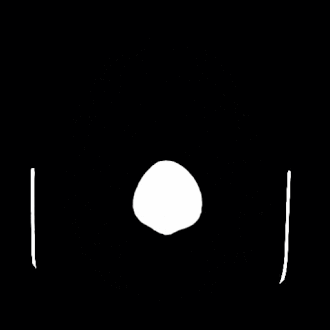
[[File:Human_brain_showning_a_colloid_cyst_in_the_third_ventricle.jpg|Human brain showing a colloid cyst in the third ventricle|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Colloid_Cyst_Cat_scan_GIF.gif|Colloid cyst CAT scan|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Central nervous system cyst''' is a pathological condition characterized by the presence of a fluid-filled sac, or [[cyst]], within the [[central nervous system]] (CNS). The CNS consists of the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]], and any cystic formation within these structures can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms. | '''Central nervous system cyst''' is a pathological condition characterized by the presence of a fluid-filled sac, or [[cyst]], within the [[central nervous system]] (CNS). The CNS consists of the [[brain]] and [[spinal cord]], and any cystic formation within these structures can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms. | ||
==Types of Central Nervous System Cysts== | ==Types of Central Nervous System Cysts== | ||
There are several types of CNS cysts, each with unique characteristics and potential complications. These include: | There are several types of CNS cysts, each with unique characteristics and potential complications. These include: | ||
* '''[[Arachnoid cyst]]s''': These are the most common type of CNS cysts. They form in the arachnoid membrane, one of the three layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord. | * '''[[Arachnoid cyst]]s''': These are the most common type of CNS cysts. They form in the arachnoid membrane, one of the three layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord. | ||
* '''[[Colloid cyst]]s''': These cysts typically occur in the third ventricle of the brain and can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to increased intracranial pressure. | * '''[[Colloid cyst]]s''': These cysts typically occur in the third ventricle of the brain and can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to increased intracranial pressure. | ||
* '''[[Dermoid cyst]]s and [[Epidermoid cyst]]s''': These are congenital cysts that are typically present at birth. They result from the inclusion of ectodermal tissue during neural tube closure. | * '''[[Dermoid cyst]]s and [[Epidermoid cyst]]s''': These are congenital cysts that are typically present at birth. They result from the inclusion of ectodermal tissue during neural tube closure. | ||
* '''[[Pineal cyst]]s''': These cysts occur in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain. Most pineal cysts are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. | * '''[[Pineal cyst]]s''': These cysts occur in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain. Most pineal cysts are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of a CNS cyst depend on its size and location. Small cysts may not cause any symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during imaging studies for other conditions. Larger cysts, or those located in certain areas of the brain or spinal cord, can cause symptoms such as [[headache]], [[seizure]]s, [[vertigo]], and neurological deficits. | The symptoms of a CNS cyst depend on its size and location. Small cysts may not cause any symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during imaging studies for other conditions. Larger cysts, or those located in certain areas of the brain or spinal cord, can cause symptoms such as [[headache]], [[seizure]]s, [[vertigo]], and neurological deficits. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of a CNS cyst typically involves imaging studies such as [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) or [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans. These studies can reveal the presence, size, and location of the cyst. In some cases, a [[lumbar puncture]] may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid. | Diagnosis of a CNS cyst typically involves imaging studies such as [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) or [[computed tomography]] (CT) scans. These studies can reveal the presence, size, and location of the cyst. In some cases, a [[lumbar puncture]] may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for a CNS cyst depends on the type of cyst, its size, and the symptoms it is causing. Options may include observation, medication to control symptoms, or surgery to remove the cyst. | Treatment for a CNS cyst depends on the type of cyst, its size, and the symptoms it is causing. Options may include observation, medication to control symptoms, or surgery to remove the cyst. | ||
== Central_nervous_system_cyst gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Human_brain_showning_a_colloid_cyst_in_the_third_ventricle.jpg|Human brain showing a colloid cyst in the third ventricle | |||
File:Colloid_Cyst_Cat_scan_GIF.gif|Colloid cyst CAT scan | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Neurology]] | * [[Neurology]] | ||
* [[Neurosurgery]] | * [[Neurosurgery]] | ||
* [[Cyst]] | * [[Cyst]] | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Pathology]] | [[Category:Pathology]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
{{Neurology-stub}} | {{Neurology-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:01, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Central nervous system cyst | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, seizures, nausea, vomiting, balance disorder, vision problems |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, brain herniation |
| Onset | Varies, can be congenital or acquired |
| Duration | Can be chronic |
| Types | Arachnoid cyst, colloid cyst, dermoid cyst, epidermoid cyst |
| Causes | Developmental anomaly, trauma, infection, tumor |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, head injury |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Brain tumor, abscess, hematoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, endoscopic fenestration, shunt placement |
| Medication | Anticonvulsant, analgesic |
| Prognosis | Varies, generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | Rare, usually due to complications |

Central nervous system cyst is a pathological condition characterized by the presence of a fluid-filled sac, or cyst, within the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, and any cystic formation within these structures can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms.
Types of Central Nervous System Cysts[edit]
There are several types of CNS cysts, each with unique characteristics and potential complications. These include:
- Arachnoid cysts: These are the most common type of CNS cysts. They form in the arachnoid membrane, one of the three layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord.
- Colloid cysts: These cysts typically occur in the third ventricle of the brain and can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to increased intracranial pressure.
- Dermoid cysts and Epidermoid cysts: These are congenital cysts that are typically present at birth. They result from the inclusion of ectodermal tissue during neural tube closure.
- Pineal cysts: These cysts occur in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain. Most pineal cysts are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of a CNS cyst depend on its size and location. Small cysts may not cause any symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during imaging studies for other conditions. Larger cysts, or those located in certain areas of the brain or spinal cord, can cause symptoms such as headache, seizures, vertigo, and neurological deficits.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a CNS cyst typically involves imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. These studies can reveal the presence, size, and location of the cyst. In some cases, a lumbar puncture may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for a CNS cyst depends on the type of cyst, its size, and the symptoms it is causing. Options may include observation, medication to control symptoms, or surgery to remove the cyst.
Central_nervous_system_cyst gallery[edit]
-
Human brain showing a colloid cyst in the third ventricle
-
Colloid cyst CAT scan
See Also[edit]


