Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= | {{SI}}<br> | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
File:Anaplastic_large_cell_lymphoma_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg| | | name = Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma | ||
| image = [[File:Anaplastic_large_cell_lymphoma_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg|alt=Micrograph of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma]] | |||
| image_size = 250px | |||
== | | alt = Micrograph of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma | ||
| caption = Micrograph of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma | |||
| field = [[Hematology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Lymphadenopathy]], [[fever]], [[weight loss]], [[night sweats]] | |||
| complications = [[Immunodeficiency]], [[infection]] | |||
| onset = Variable | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = [[Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma]], [[Systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma]] | |||
| causes = Unknown, possible genetic mutations | |||
| risks = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[immunosuppression]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Biopsy]], [[immunohistochemistry]] | |||
| differential = [[Hodgkin lymphoma]], [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]], [[Lymphoblastic lymphoma]] | |||
| prevention = None | |||
| treatment = [[Chemotherapy]], [[radiation therapy]], [[stem cell transplant]] | |||
| medication = [[Brentuximab vedotin]], [[CHOP chemotherapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on subtype and stage | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma''' (ALCL) is a type of [[non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] that is characterized by the presence of large, atypical lymphoid cells. It is a rare form of lymphoma that can occur in both children and adults. ALCL is classified as a T-cell lymphoma, meaning it originates from [[T lymphocytes]], a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. | '''Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma''' (ALCL) is a type of [[non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] that is characterized by the presence of large, atypical lymphoid cells. It is a rare form of lymphoma that can occur in both children and adults. ALCL is classified as a T-cell lymphoma, meaning it originates from [[T lymphocytes]], a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. | ||
=== Classification === | === Classification === | ||
ALCL is divided into two main types based on the presence or absence of a specific genetic abnormality involving the [[anaplastic lymphoma kinase]] (ALK) gene: | ALCL is divided into two main types based on the presence or absence of a specific genetic abnormality involving the [[anaplastic lymphoma kinase]] (ALK) gene: | ||
* '''ALK-positive ALCL''': This type is more common in children and young adults. It is characterized by the presence of a translocation involving the ALK gene, which leads to the expression of an abnormal ALK protein that promotes cell growth and survival. | * '''ALK-positive ALCL''': This type is more common in children and young adults. It is characterized by the presence of a translocation involving the ALK gene, which leads to the expression of an abnormal ALK protein that promotes cell growth and survival. | ||
* '''ALK-negative ALCL''': This type is more common in older adults and does not have the ALK gene rearrangement. It tends to have a more aggressive clinical course compared to ALK-positive ALCL. | * '''ALK-negative ALCL''': This type is more common in older adults and does not have the ALK gene rearrangement. It tends to have a more aggressive clinical course compared to ALK-positive ALCL. | ||
=== Clinical Presentation === | === Clinical Presentation === | ||
Patients with ALCL may present with a variety of symptoms, including: | Patients with ALCL may present with a variety of symptoms, including: | ||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]]: Swelling of the lymph nodes, which may be painless. | * [[Lymphadenopathy]]: Swelling of the lymph nodes, which may be painless. | ||
* [[B symptoms]]: Fever, night sweats, and weight loss. | * [[B symptoms]]: Fever, night sweats, and weight loss. | ||
* Extranodal involvement: ALCL can affect organs outside the lymphatic system, such as the skin, liver, lungs, and bones. | * Extranodal involvement: ALCL can affect organs outside the lymphatic system, such as the skin, liver, lungs, and bones. | ||
=== Diagnosis === | === Diagnosis === | ||
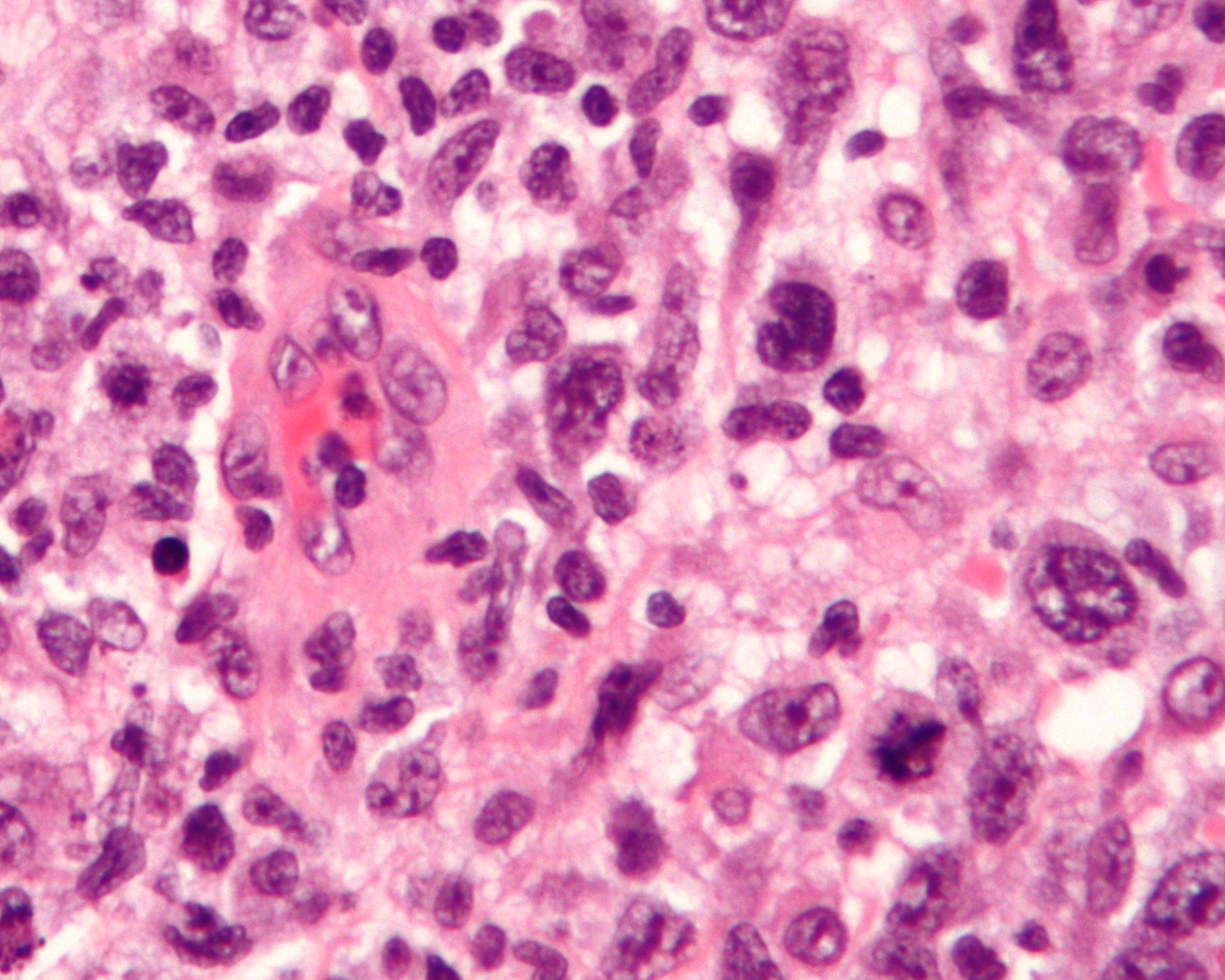
The diagnosis of ALCL is made through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and [[biopsy]] of affected tissue. Histological examination reveals large, pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm and horseshoe-shaped nuclei. Immunohistochemistry is used to detect the expression of CD30, a marker that is typically positive in ALCL cells. | The diagnosis of ALCL is made through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and [[biopsy]] of affected tissue. Histological examination reveals large, pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm and horseshoe-shaped nuclei. Immunohistochemistry is used to detect the expression of CD30, a marker that is typically positive in ALCL cells. | ||
=== Treatment === | === Treatment === | ||
The treatment of ALCL depends on the subtype and stage of the disease. Common treatment options include: | The treatment of ALCL depends on the subtype and stage of the disease. Common treatment options include: | ||
* [[Chemotherapy]]: Regimens such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) are commonly used. | * [[Chemotherapy]]: Regimens such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) are commonly used. | ||
* Targeted therapy: For ALK-positive ALCL, ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib may be used. | * Targeted therapy: For ALK-positive ALCL, ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib may be used. | ||
* [[Radiation therapy]]: May be used in certain cases, especially for localized disease. | * [[Radiation therapy]]: May be used in certain cases, especially for localized disease. | ||
* [[Stem cell transplantation]]: Considered in cases of relapsed or refractory ALCL. | * [[Stem cell transplantation]]: Considered in cases of relapsed or refractory ALCL. | ||
=== Prognosis === | === Prognosis === | ||
The prognosis of ALCL varies depending on the subtype and other factors such as age and overall health. ALK-positive ALCL generally has a better prognosis compared to ALK-negative ALCL. Long-term survival rates are higher in children and young adults compared to older patients. | The prognosis of ALCL varies depending on the subtype and other factors such as age and overall health. ALK-positive ALCL generally has a better prognosis compared to ALK-negative ALCL. Long-term survival rates are higher in children and young adults compared to older patients. | ||
== Related Pages == | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] | * [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 47: | ||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | * [[Lymphadenopathy]] | ||
* [[Chemotherapy]] | * [[Chemotherapy]] | ||
{{Lymphoma}} | {{Lymphoma}} | ||
[[Category:Lymphoma]] | [[Category:Lymphoma]] | ||
[[Category:Hematology]] | [[Category:Hematology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:50, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lymphadenopathy, fever, weight loss, night sweats |
| Complications | Immunodeficiency, infection |
| Onset | Variable |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, Systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma |
| Causes | Unknown, possible genetic mutations |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, immunosuppression |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, immunohistochemistry |
| Differential diagnosis | Hodgkin lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Lymphoblastic lymphoma |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplant |
| Medication | Brentuximab vedotin, CHOP chemotherapy |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on subtype and stage |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is characterized by the presence of large, atypical lymphoid cells. It is a rare form of lymphoma that can occur in both children and adults. ALCL is classified as a T-cell lymphoma, meaning it originates from T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system.
Classification[edit]
ALCL is divided into two main types based on the presence or absence of a specific genetic abnormality involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene:
- ALK-positive ALCL: This type is more common in children and young adults. It is characterized by the presence of a translocation involving the ALK gene, which leads to the expression of an abnormal ALK protein that promotes cell growth and survival.
- ALK-negative ALCL: This type is more common in older adults and does not have the ALK gene rearrangement. It tends to have a more aggressive clinical course compared to ALK-positive ALCL.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with ALCL may present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes, which may be painless.
- B symptoms: Fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
- Extranodal involvement: ALCL can affect organs outside the lymphatic system, such as the skin, liver, lungs, and bones.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of ALCL is made through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and biopsy of affected tissue. Histological examination reveals large, pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm and horseshoe-shaped nuclei. Immunohistochemistry is used to detect the expression of CD30, a marker that is typically positive in ALCL cells.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of ALCL depends on the subtype and stage of the disease. Common treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy: Regimens such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) are commonly used.
- Targeted therapy: For ALK-positive ALCL, ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib may be used.
- Radiation therapy: May be used in certain cases, especially for localized disease.
- Stem cell transplantation: Considered in cases of relapsed or refractory ALCL.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of ALCL varies depending on the subtype and other factors such as age and overall health. ALK-positive ALCL generally has a better prognosis compared to ALK-negative ALCL. Long-term survival rates are higher in children and young adults compared to older patients.
Related Pages[edit]
| Lymphomas | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This lymphoma-related article is a stub.
|