Microphthalmia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Developmental disorder of the eye}} | {{short description|Developmental disorder of the eye}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | {{Infobox medical condition (new) | ||
| name | | name = Microphthalmia | ||
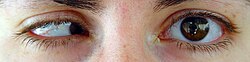
| image | | image = Microphthalmia1.jpg | ||
| caption | | caption = Unilateral Microphthalmia | ||
| symptoms | | symptoms = Small eyes, abnormal eye anatomy, blindness | ||
| complications | | complications = Vision impairment, associated craniofacial defects | ||
| onset | | onset = Congenital (present at birth) | ||
| duration | | duration = Lifelong | ||
| types | | types = Unilateral, bilateral | ||
| causes | | causes = Genetic mutations, maternal infections during pregnancy (e.g., rubella, CMV) | ||
| risks | | risks = Autosomal dominant or recessive inheritance, environmental factors (e.g., prenatal infections) | ||
| diagnosis | | diagnosis = Clinical findings, imaging (CT or MRI), genetic testing (e.g., FGF3, MITF genes) | ||
| differential | | differential = Anophthalmia, nanophthalmos, other congenital eye malformations | ||
| prevention | | prevention = Early prenatal care, avoidance of teratogenic exposures during pregnancy | ||
| treatment | | treatment = Early intervention for visual and developmental support, potential reconstructive surgery | ||
| medication | | medication = | ||
| prognosis | | prognosis = Dependent on severity and associated malformations | ||
| frequency | | frequency = Rare, prevalence varies by population | ||
| deaths | | deaths = Not typically fatal, but associated complications may affect quality of life | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:Goddard 11 (bottom).jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | [[File:Goddard 11 (bottom).jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Microphthalmus congenitus.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb|left]] | [[File:Microphthalmus congenitus.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb|left]] | ||
[[File:Microphthalmia-500px.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | [[File:Microphthalmia-500px.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | ||
==Presentation== | '''Microphthalmia''' (Greek: μικρός ''mikros'' = small; ὀφθαλμός ''ophthalmos'' = eye), also referred to as microphthalmos, is a congenital eye disorder characterized by abnormally small eyes, which may result in a range of anatomical malformations. The condition can affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral), leading to varying degrees of vision impairment or blindness. Microphthalmia is distinct from [[nanophthalmos]], where the eyes are small but without additional structural abnormalities. | ||
== Presentation == | |||
Microphthalmia is often diagnosed at birth or in early childhood, where the eyes are visibly smaller than normal and may exhibit developmental malformations. The affected eyes may have defects in the retina, optic nerve, or other ocular structures. In severe cases, microphthalmia can result in complete blindness, though some individuals may have limited vision depending on the severity of the condition. | |||
The incidence of microphthalmia is approximately 14 per 100,000 births, and it is found in 3-11% of blind children. | |||
== Causes == | |||
Microphthalmia can result from genetic mutations or environmental factors, particularly during pregnancy. The following are common causes: | |||
* '''Genetic causes''': Microphthalmia is often caused by mutations in several key genes that play a role in eye development: | |||
* '''FGF3''': Fibroblast growth factor 3, mutations in this gene are associated with microphthalmia in some cases. | |||
* '''MITF''': Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, mutations can lead to isolated microphthalmia or syndromic forms with other craniofacial anomalies. | |||
* '''PAX6''': A gene involved in eye development, mutations may cause microphthalmia along with other developmental issues. | |||
* '''SOX2''': A critical gene for eye and pituitary development, with mutations leading to various ocular anomalies. | |||
* '''GDF3, BMP4, and other transcription factors''': These genes regulate eye growth and differentiation. | |||
* '''Environmental factors''': Exposure to certain infections during pregnancy can cause microphthalmia. Known teratogenic infections include: | |||
* '''Herpes simplex virus''' | |||
* '''Rubella (German measles)''' | |||
* '''Cytomegalovirus (CMV)''' | |||
* '''Fetal alcohol syndrome''' | |||
These environmental factors may disrupt the development of the eyes during pregnancy, leading to microphthalmia. | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | |||
Signs and symptoms of microphthalmia depend on the severity and whether one or both eyes are affected. Common symptoms include: | |||
* '''Small eyes''' (uni- or bilateral) | |||
* '''Abnormal eye structures''' (e.g., malformed retina, optic nerve) | |||
* '''Vision impairment''' or complete blindness | |||
* '''Craniofacial abnormalities''' (e.g., microtia, microdontia) | |||
* '''Potential developmental delays''' due to visual and sensory impairment | |||
In more severe cases, the affected individuals may have associated abnormalities in the skeletal and craniofacial structures. | |||
==Diagnosis== | == Diagnosis == | ||
Microphthalmia is diagnosed through: | |||
* '''Clinical examination''': A physical exam reveals the presence of abnormally small eyes and other possible malformations. | |||
* '''Imaging''': A [[CT scan]] or [[MRI]] can be used to visualize the eye structures and confirm the absence or underdevelopment of key ocular components. | |||
* '''Genetic testing''': Molecular testing for mutations in genes like FGF3, MITF, PAX6, and SOX2 can confirm the genetic basis of microphthalmia. Testing may also identify other syndromic features or chromosomal abnormalities. | |||
Early diagnosis is essential for managing the condition and initiating appropriate interventions. | |||
== Treatment == | |||
There is no cure for microphthalmia, but several interventions can support the individual's quality of life: | |||
* '''Early intervention programs''': Children diagnosed with microphthalmia may benefit from early intervention programs tailored to children with sensory impairments. These programs often focus on language development, cognitive skills, and socialization. | |||
* | * '''Visual aids''': Low-vision devices and strategies, such as tactile books, magnifiers, and auditory aids, can be helpful for those with limited vision. | ||
* '''Surgical options''': In cases where the affected eye has anatomical malformations, surgical reconstruction of the orbit or other facial features may be considered. | |||
* '''Cochlear implants''': If there is associated hearing loss, cochlear implantation may be considered as a treatment option. | |||
* '''Cochlear implantation and visual aids''': For some individuals with profound vision impairment, alternative forms of communication such as braille and sign language may also be introduced as part of treatment. | |||
== | '''Cochlear implants and other technologies''' can provide varying degrees of sensory restoration, though the success of such interventions is dependent on the specific case. | ||
== Prevention == | |||
Although microphthalmia cannot always be prevented, prenatal care plays an essential role in minimizing environmental risks: | |||
* '''Prenatal care''': Regular monitoring of maternal health during pregnancy to prevent infections, manage risk factors, and screen for teratogenic exposures. | |||
* '''Genetic counseling''': For families with a known history of genetic mutations associated with microphthalmia, genetic counseling can help assess the risk of recurrence in future pregnancies. | |||
== Prognosis == | |||
The prognosis for individuals with microphthalmia varies depending on the severity of the condition and associated malformations. Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life, particularly with educational and developmental support. In severe cases, microphthalmia may lead to profound blindness and associated developmental delays. | |||
== Epidemiology == | |||
Microphthalmia is a rare congenital condition. The incidence is estimated to be approximately 10.8 per 100,000 births in the United Kingdom, with variations in different populations. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Congenital eye disorders]] | |||
* [[Microtia]] | |||
* [[Anophthalmia]] | |||
* [[Waardenburg syndrome type 2]] | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1378/ GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH entry on Microphthalmia Overview]() | |||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=gene&part=microph-lsd GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH entry on Microphthalmia with Linear Skin Defects Syndrome] | |||
* [[OMIM]] - Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man | |||
{{Medical resources | {{Medical resources | ||
| | | DiseasesDB = 29618 | ||
| | | ICD10 = Q11.2 | ||
| | | ICD9 = 743.1 | ||
| OMIM = | |||
| | | GeneReviewsNBK = NBK1378 | ||
| GeneReviewsName = Anophthalmia / Microphthalmia Overview | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Genetic disorders | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Eye disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
{{disease-stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 2 April 2025
Developmental disorder of the eye



Microphthalmia (Greek: μικρός mikros = small; ὀφθαλμός ophthalmos = eye), also referred to as microphthalmos, is a congenital eye disorder characterized by abnormally small eyes, which may result in a range of anatomical malformations. The condition can affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral), leading to varying degrees of vision impairment or blindness. Microphthalmia is distinct from nanophthalmos, where the eyes are small but without additional structural abnormalities.
Presentation[edit]
Microphthalmia is often diagnosed at birth or in early childhood, where the eyes are visibly smaller than normal and may exhibit developmental malformations. The affected eyes may have defects in the retina, optic nerve, or other ocular structures. In severe cases, microphthalmia can result in complete blindness, though some individuals may have limited vision depending on the severity of the condition.
The incidence of microphthalmia is approximately 14 per 100,000 births, and it is found in 3-11% of blind children.
Causes[edit]
Microphthalmia can result from genetic mutations or environmental factors, particularly during pregnancy. The following are common causes:
- Genetic causes: Microphthalmia is often caused by mutations in several key genes that play a role in eye development:
- FGF3: Fibroblast growth factor 3, mutations in this gene are associated with microphthalmia in some cases.
- MITF: Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, mutations can lead to isolated microphthalmia or syndromic forms with other craniofacial anomalies.
- PAX6: A gene involved in eye development, mutations may cause microphthalmia along with other developmental issues.
- SOX2: A critical gene for eye and pituitary development, with mutations leading to various ocular anomalies.
- GDF3, BMP4, and other transcription factors: These genes regulate eye growth and differentiation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain infections during pregnancy can cause microphthalmia. Known teratogenic infections include:
- Herpes simplex virus
- Rubella (German measles)
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Fetal alcohol syndrome
These environmental factors may disrupt the development of the eyes during pregnancy, leading to microphthalmia.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Signs and symptoms of microphthalmia depend on the severity and whether one or both eyes are affected. Common symptoms include:
- Small eyes (uni- or bilateral)
- Abnormal eye structures (e.g., malformed retina, optic nerve)
- Vision impairment or complete blindness
- Craniofacial abnormalities (e.g., microtia, microdontia)
- Potential developmental delays due to visual and sensory impairment
In more severe cases, the affected individuals may have associated abnormalities in the skeletal and craniofacial structures.
Diagnosis[edit]
Microphthalmia is diagnosed through:
- Clinical examination: A physical exam reveals the presence of abnormally small eyes and other possible malformations.
- Imaging: A CT scan or MRI can be used to visualize the eye structures and confirm the absence or underdevelopment of key ocular components.
- Genetic testing: Molecular testing for mutations in genes like FGF3, MITF, PAX6, and SOX2 can confirm the genetic basis of microphthalmia. Testing may also identify other syndromic features or chromosomal abnormalities.
Early diagnosis is essential for managing the condition and initiating appropriate interventions.
Treatment[edit]
There is no cure for microphthalmia, but several interventions can support the individual's quality of life:
- Early intervention programs: Children diagnosed with microphthalmia may benefit from early intervention programs tailored to children with sensory impairments. These programs often focus on language development, cognitive skills, and socialization.
- Visual aids: Low-vision devices and strategies, such as tactile books, magnifiers, and auditory aids, can be helpful for those with limited vision.
- Surgical options: In cases where the affected eye has anatomical malformations, surgical reconstruction of the orbit or other facial features may be considered.
- Cochlear implants: If there is associated hearing loss, cochlear implantation may be considered as a treatment option.
- Cochlear implantation and visual aids: For some individuals with profound vision impairment, alternative forms of communication such as braille and sign language may also be introduced as part of treatment.
Cochlear implants and other technologies can provide varying degrees of sensory restoration, though the success of such interventions is dependent on the specific case.
Prevention[edit]
Although microphthalmia cannot always be prevented, prenatal care plays an essential role in minimizing environmental risks:
- Prenatal care: Regular monitoring of maternal health during pregnancy to prevent infections, manage risk factors, and screen for teratogenic exposures.
- Genetic counseling: For families with a known history of genetic mutations associated with microphthalmia, genetic counseling can help assess the risk of recurrence in future pregnancies.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with microphthalmia varies depending on the severity of the condition and associated malformations. Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life, particularly with educational and developmental support. In severe cases, microphthalmia may lead to profound blindness and associated developmental delays.
Epidemiology[edit]
Microphthalmia is a rare congenital condition. The incidence is estimated to be approximately 10.8 per 100,000 births in the United Kingdom, with variations in different populations.
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH entry on Microphthalmia Overview()
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH entry on Microphthalmia with Linear Skin Defects Syndrome
- OMIM - Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man