Darodipine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
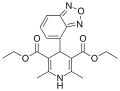
File:Darodipine structure.svg|Darodipine structure | File:Darodipine structure.svg|Darodipine structure | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:16, 16 March 2025
Darodipine (also known as PY 108-068) is a calcium channel blocker that is used in the treatment of hypertension. It is a dihydropyridine derivative and is similar to other calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, felodipine, and isradipine.
Pharmacology[edit]
Darodipine inhibits the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. It binds to dihydropyridine and phenylalkylamine binding sites. The binding is voltage-dependent and is enhanced at depolarized membrane potentials.
Clinical Use[edit]
Darodipine is used in the treatment of hypertension. It lowers blood pressure by relaxing the smooth muscle in the walls of the arteries, causing them to open wider. This reduces the pressure in the arteries, making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
Side Effects[edit]
Like other calcium channel blockers, darodipine can cause a number of side effects. These can include dizziness, flushing, headache, nausea, palpitations, and edema. In rare cases, it can cause serious side effects such as arrhythmia and hypotension.
See Also[edit]
|
|
|
References[edit]
<references />
External Links[edit]
- Darodipine on Drugs.com
- Darodipine on PubChem
-
Darodipine structure