Root mean square: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Electrical Engineering]] | [[Category:Electrical Engineering]] | ||
[[Category:Audio Engineering]] | [[Category:Audio Engineering]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Waveforms.svg|Waveforms | |||
File:Dutycycle.svg|Dutycycle | |||
File:Sine wave voltages.svg|Sine wave voltages | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 06:09, 3 March 2025
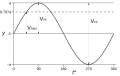
Root mean square (RMS) is a statistical measure that is commonly used in various fields to quantify the average magnitude of a set of values. It is particularly useful in analyzing data that fluctuates over time, such as electrical signals or sound waves. The RMS value provides a way to express the overall "size" or "amplitude" of the data set, taking into account both positive and negative values.
Definition[edit]
The root mean square is calculated by taking the square root of the mean of the squared values in a data set. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
{{{1}}} }
where n is the number of values in the data set, and x_i represents each individual value.
Applications[edit]
Electrical Engineering[edit]
In electrical engineering, the RMS value is commonly used to measure the voltage or current of an alternating current (AC) signal. Since AC signals continuously change their polarity, simply taking the average value would not accurately represent the signal's magnitude. By calculating the RMS value, engineers can determine the effective voltage or current that would produce the same amount of power in a direct current (DC) circuit.
Audio Engineering[edit]
In audio engineering, the RMS value is used to measure the amplitude of sound waves. By calculating the RMS value of an audio signal, engineers can determine the average power or loudness of the sound. This information is crucial in various applications, such as audio recording, mixing, and mastering.
Statistics[edit]
In statistics, the RMS value is often used as a measure of dispersion or variability within a data set. It provides a way to quantify the spread of values around the mean. By comparing the RMS values of different data sets, statisticians can assess the relative variability and make informed decisions based on the data.
Advantages[edit]
The use of RMS has several advantages in various fields:
- Symmetry - The RMS value takes into account both positive and negative values, making it suitable for analyzing data with alternating polarity.
- Meaningful representation - Unlike the average value, which can be influenced by extreme outliers, the RMS value provides a more representative measure of the overall magnitude of the data set.
- Compatibility - The RMS value can be easily compared and combined with other statistical measures, such as standard deviation or variance, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the data.
Limitations[edit]
While the RMS value is a useful measure, it is important to be aware of its limitations:
- Non-linearity - The RMS value assumes that the data set follows a linear relationship. In cases where the data exhibits non-linear behavior, alternative measures may be more appropriate.
- Context-dependency - The interpretation of the RMS value depends on the specific application and context. It is essential to consider the domain-specific requirements and limitations when using RMS as a measure.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
Waveforms
-
Dutycycle
-
Sine wave voltages