Histidine decarboxylase: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Histidine metabolism]] | [[Category:Histidine metabolism]] | ||
[[Category:Human proteins]] | [[Category:Human proteins]] | ||
== Histidine decarboxylase gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:HDC 3d Ray Image.png|HDC 3d Ray Image | |||
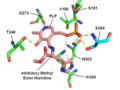
File:HDC Active Site Diagram.tif|HDC Active Site Diagram | |||
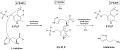
File:HDC mechanism.tif|HDC mechanism | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:23, 3 March 2025
Histidine decarboxylase (HDC) is an enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation of histidine, an amino acid, to produce histamine, a biogenic amine. This enzyme is part of the larger family of lyase enzymes, specifically the carboxy-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-histidine carboxy-lyase (histamine-forming). Other names in common use include L-histidine decarboxylase, and histidine decarboxylase. This enzyme participates in histidine metabolism and is also involved in the biosynthesis of histamine, a key component in the regulation of immune responses and physiological functions in the gut.
Structure[edit]
Histidine decarboxylase is a dimer composed of identical subunits. Each subunit is composed of three domains: a pyridoxal phosphate-binding domain, a regulatory domain, and a catalytic domain. The pyridoxal phosphate-binding domain is responsible for the enzyme's catalytic activity, while the regulatory domain controls the enzyme's activity.
Function[edit]
Histidine decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of histidine to produce histamine. Histamine plays a crucial role in the body, acting as a neurotransmitter to send signals in the nervous system, and as a mediator of inflammatory responses. It is also involved in the regulation of stomach acid production.
Clinical significance[edit]
Alterations in histidine decarboxylase activity have been associated with various diseases. For instance, increased HDC activity has been observed in gastric cancer and migraines, while decreased activity has been linked to schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease. HDC inhibitors are being studied as potential treatments for these conditions.
See also[edit]
| Enzymes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Histidine decarboxylase gallery[edit]
-
HDC 3d Ray Image
-
HDC Active Site Diagram
-
HDC mechanism