Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | [[Category:Pharmacology]] | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
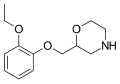
== Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Atomoxetine structure.svg|Atomoxetine structure | |||
File:Reboxetine.svg|Reboxetine | |||
File:Viloxazine structure.svg|Viloxazine structure | |||
File:SAR .png|SAR | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:08, 3 March 2025
Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRI) is a class of antidepressant drugs used in the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other mood disorders. SNRIs work by increasing the levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline) in the brain, which is thought to have a good effect on mood. This is achieved by inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine, allowing more of it to be available for transmitting messages between nerve cells.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
SNRIs block the reuptake of norepinephrine into the presynaptic neuron, leading to an increase in the concentration of norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft. This enhances neurotransmission and is believed to contribute to the antidepressant effects of these medications. Some SNRIs also have secondary effects on the reuptake of serotonin, another neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation, but their primary target is norepinephrine pathways.
Indications[edit]
While the primary indication for SNRIs is the treatment of MDD, they are also used for a variety of other conditions, including:
- Anxiety Disorders
- Chronic Pain syndromes, such as Fibromyalgia and Neuropathic Pain
- ADHD in some cases
- Menopausal Symptoms, particularly hot flashes
Examples of SNRIs[edit]
Some well-known SNRIs include:
- Venlafaxine, which was one of the first SNRIs to be approved
- Duloxetine, known for its use in treating depression, anxiety, and certain types of chronic pain
- Desvenlafaxine, a metabolite of venlafaxine
- Levomilnacipran, a newer addition to the class
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of SNRIs can include nausea, dry mouth, dizziness, headache, and insomnia. Due to their effect on norepinephrine, they can also increase blood pressure and heart rate in some individuals. It is important for patients to be monitored for these effects, especially those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Comparison with Other Antidepressants[edit]
SNRIs are often compared to SSRIs, another class of antidepressants that primarily affect serotonin levels. While both classes are effective for treating depression, SNRIs may be chosen over SSRIs for patients who have not responded to SSRIs or those who have specific symptoms such as chronic pain.
Conclusion[edit]
Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors represent an important class of medications in the management of depression and other mood disorders. Their unique mechanism of action, focusing on norepinephrine reuptake inhibition, offers an alternative or adjunct to other antidepressant therapies, particularly for patients with specific clinical profiles or those who have not responded to other treatments.
Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor gallery[edit]
-
Atomoxetine structure
-
Reboxetine
-
Viloxazine structure
-
SAR