BOM (psychedelic): Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Alexander Shulgin]] | [[Category:Alexander Shulgin]] | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
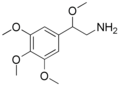
File:3,4,5,beta-tetramethoxyphenethylamine.png|3,4,5,beta-tetramethoxyphenethylamine | |||
File:BOM-3d-sticks.png|BOM-3d-sticks | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:10, 25 February 2025
BOM (psychedelic)
BOM, also known as 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine, is a psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is part of the DOB family of psychedelic compounds, first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
Chemistry[edit]
BOM is a brominated compound, derived from amphetamine. Its full chemical name is 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine. The drug has structural similarities to other psychedelic amphetamines such as DOB and DOC.
Pharmacology[edit]
BOM acts as a serotonin receptor agonist. It has a high affinity for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, which are thought to be primarily responsible for its psychedelic effects. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a complex interplay of neurotransmitter systems.
Effects[edit]
The effects of BOM are similar to those of other psychedelic amphetamines. These can include hallucinations, altered perception of time and space, enhanced introspection, and emotional intensification. The duration of effects can vary widely depending on dose, but typically range from 6 to 12 hours.
Risks[edit]
As with all psychedelic drugs, BOM carries risks. These can include psychological distress, dangerous behavior due to altered perceptions, and potential for abuse. There is also a risk of physical harm due to the drug's amphetamine base, including cardiovascular issues and neurotoxicity.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of BOM varies by country. In many places, it is a controlled substance, making its manufacture, distribution, and use illegal.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
3,4,5,beta-tetramethoxyphenethylamine
-
BOM-3d-sticks