Crosslinking of DNA: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{Biochem-stub}} | {{Biochem-stub}} | ||
{{Molbio-stub}} | {{Molbio-stub}} | ||
== Crosslinking_of_DNA == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Crosslinking.jpg|Crosslinking | |||
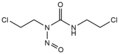
File:Nitrogen_Mustard.tif|Nitrogen Mustard | |||
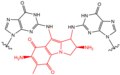
File:Cisplatin_Corsslink.tif|Cisplatin Crosslink | |||
File:Carmustine_(BNCU).tif|Carmustine (BNCU) | |||
File:Carmustine_Crosslink.tif|Carmustine Crosslink | |||
File:Mitomycin.svg|Mitomycin | |||
File:Mitomycin_Crosslink.tif|Mitomycin Crosslink | |||
File:Psolaren_Structure.tif|Psolaren Structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:04, 25 February 2025
Crosslinking of DNA is a critical biological process that involves the formation of covalent bonds between two DNA strands. This process is essential for maintaining the stability and integrity of the DNA molecule, and plays a significant role in various biological functions such as DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell division.
Overview[edit]
Crosslinking of DNA occurs when a covalent bond is formed between two DNA strands. This bond can be formed either within the same DNA molecule (intrastrand crosslink) or between two different DNA molecules (interstrand crosslink). The formation of these crosslinks can be induced by various factors, including exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, or as a result of certain biological processes.
Types of DNA Crosslinks[edit]
Intrastrand Crosslinks[edit]
Intrastrand crosslinks occur when a covalent bond is formed within the same DNA molecule. This type of crosslink can cause significant distortion to the DNA helix, which can interfere with the normal functioning of the DNA molecule.
Interstrand Crosslinks[edit]
Interstrand crosslinks occur when a covalent bond is formed between two different DNA molecules. This type of crosslink is particularly damaging, as it can prevent the separation of the DNA strands, which is necessary for DNA replication and transcription.
Biological Significance[edit]
Crosslinking of DNA plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the DNA molecule. It is also involved in various biological functions such as DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell division. However, excessive or inappropriate crosslinking can lead to DNA damage, which can cause mutations and lead to various diseases, including cancer.
DNA Crosslink Repair[edit]
Cells have developed several mechanisms to repair DNA crosslinks. These mechanisms include the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway, the base excision repair (BER) pathway, and the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway. These repair pathways are essential for maintaining the integrity of the DNA molecule and preventing the accumulation of DNA damage.
See Also[edit]

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This molecular biology related article is a stub.
Crosslinking_of_DNA[edit]
-
Crosslinking
-
Nitrogen Mustard
-
Cisplatin Crosslink
-
Carmustine (BNCU)
-
Carmustine Crosslink
-
Mitomycin
-
Mitomycin Crosslink
-
Psolaren Structure