Bulbospongiosus muscle: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Sexual anatomy]] | [[Category:Sexual anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Perineum]] | [[Category:Perineum]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray407.png|Gray407 | |||
File:Gray542.png|Gray542 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:51, 25 February 2025
Bulbospongiosus muscle is a muscle of the perineum found in both males and females. It has different functions depending on the sex of the individual.
Etymology[edit]
The term "bulbospongiosus" is derived from the Latin words "bulbus", meaning "bulb", and "spongiosus", meaning "spongy". This refers to the muscle's location and texture.
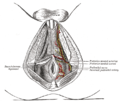
Anatomy[edit]
The bulbospongiosus muscle is located in the pelvic region, covering the bulb of penis in males and the bulb of vestibule in females. It is a superficial muscle, meaning it is close to the surface of the body.
In males, the bulbospongiosus muscle contributes to erection, ejaculation, and micturition. It does this by compressing the bulb of the penis, aiding in the expulsion of semen and urine.
In females, the bulbospongiosus muscle constricts the vagina during sexual activity. It also assists in childbirth by compressing the bulb of the vestibule, which aids in the expulsion of the fetus.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the bulbospongiosus muscle can result in sexual dysfunction in both males and females. In males, this can manifest as erectile dysfunction or difficulty with ejaculation. In females, damage to the bulbospongiosus muscle can result in vaginismus, a condition characterized by involuntary contractions of the vagina.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />