Immunoradiometric assay: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Radioactivity-stub}} | {{Radioactivity-stub}} | ||
{{nt}} | {{nt}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Immunoradiometric_assay.png|Immunoradiometric assay | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:51, 24 February 2025
Immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) is a type of radioimmunoassay that uses radioactive isotopes to measure the concentration of specific antigens in a sample. It is a highly sensitive and specific method used in clinical laboratories for the detection and quantification of a wide range of substances, including hormones, drugs, and proteins.
History[edit]
The concept of IRMA was first introduced in the 1970s as an improvement over the existing radioimmunoassay techniques. The development of IRMA was a significant advancement in the field of immunoassay technology, providing a more accurate and reliable method for measuring antigen concentrations.
Principle[edit]
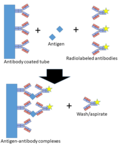
IRMA is based on the principle of immunochemistry, which involves the interaction between an antigen and its corresponding antibody. In IRMA, the antigen in the sample is sandwiched between two antibodies. One of these antibodies is labeled with a radioactive isotope, while the other is attached to a solid phase. The amount of radioactivity is directly proportional to the concentration of the antigen in the sample.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure for IRMA involves several steps. First, the sample is incubated with the solid phase antibody. After a period of time, the unbound substances are washed away. The radioactive-labeled antibody is then added and allowed to bind to the antigen. After another incubation period, the unbound labeled antibodies are washed away. The amount of radioactivity is then measured, providing a quantitative measurement of the antigen concentration.
Applications[edit]
IRMA is used in a variety of applications in both clinical and research settings. It is commonly used in the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases, including cancer, thyroid disorders, and infectious diseases. In research, IRMA is used to measure the levels of various substances in biological samples, aiding in the understanding of various biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
One of the main advantages of IRMA is its high sensitivity and specificity. It can detect very low concentrations of antigens, making it a valuable tool in the diagnosis of diseases. However, the use of radioactive isotopes poses potential health risks and requires special handling and disposal procedures. Additionally, IRMA can be time-consuming and requires a high level of technical expertise.
See Also[edit]

This article is a immunology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!

This article is a radioactivity–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Immunoradiometric assay