Rhamnose: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Alpha-L-Rhamnopyranose.svg|Alpha-L-Rhamnopyranose | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:45, 23 February 2025
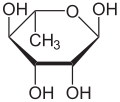
Rhamnose is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl-pentose or a 6-deoxy-hexose. Rhamnose occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose (6-deoxy-L-mannose). This is unusual, since most of the naturally occurring sugars are in D-form. Exceptions are the mucopolysaccharides and rhamnose itself.
Structure and properties[edit]
Rhamnose can exist in both a pyranose (ring) form and a furanose (ring) form. The pyranose form is more stable. Rhamnose is a component of many natural compounds including flavonoids, terpenoids, and glycosides. It is also used in the commercial production of certain chemicals.
Biological role[edit]
Rhamnose is an important part of the cell wall of some bacteria. It is also a component of the antigenic outer lipopolysaccharides present in the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. In plants, rhamnose is a component of pectin and is important for plant growth and development.
Industrial use[edit]
Rhamnose is used in the food industry as a flavoring agent and in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of drugs. It is also used in the cosmetic industry for the production of skin care products.