Big data: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{Information technology}} | {{Information technology}} | ||
{{Data-stub}} | {{Data-stub}} | ||
== Big_data == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Hilbert_InfoGrowth.png|Hilbert InfoGrowth | |||
File:Big_Data.png|Big Data | |||
File:2013-09-11_Bus_wrapped_with_SAP_Big_Data_parked_outside_IDF13_(9730051783).jpg|Bus wrapped with SAP Big Data | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:58, 23 February 2025
Big Data refers to extremely large data sets that may be analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially relating to human behavior and interactions. The term often refers simply to the use of predictive analytics, user behavior analytics, or certain other advanced data analytics methods that extract value from data, and seldom to a particular size of data set.
Definition[edit]
The term big data is often used to describe a collection of data that is huge in volume and yet growing exponentially with time. It is a data with so large size and complexity that none of traditional data management tools can store it or process it efficiently.
Characteristics[edit]
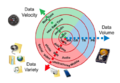
Big data can be characterized by 4Vs:
- Volume: The quantity of generated and stored data. The size of the data determines the value and potential insight, and whether it can be considered big data or not.
- Velocity: The speed at which the data is generated and processed to meet the demands and challenges that lie in the path of growth and development.
- Variety: The type and nature of the data. This helps people who analyze it to effectively use the resulting insight. Big data can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured.
- Veracity: The quality of captured data can vary greatly, affecting accurate analysis.
Applications[edit]
Big data is used in many sectors and industries where the amount of data is too large or it moves too fast or it exceeds current processing capacity. Some of the fields where big data is used include:
- Healthcare: Patient records, treatment plans, prescription information are just few types of data that can be analyzed and used to improve service and patient care.
- Retail: Customer buying habits can be predicted and new trends can be identified.
- Manufacturing: Sensors and other devices used in the manufacturing process generate plenty of data, big data tools can help optimize the manufacturing process and also save time, money and resources.
- Government: Big data can be used to improve service, detect fraud and improve performance in public sector.
Challenges[edit]
Despite its potential benefits, big data also presents challenges in terms of data privacy, data security, data analysis, data storage, data transfer, and data sharing.
See also[edit]
| Information technology topics | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This Information technology related article is a stub.
|
This data related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Big_data[edit]
-
Hilbert InfoGrowth
-
Big Data
-
Bus wrapped with SAP Big Data