Nalodeine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
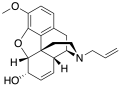
File:Nalodeine Structure.svg|Nalodeine | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Nalodeine Structure.svg|Nalodeine | File:Nalodeine Structure.svg|Nalodeine | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:45, 20 February 2025
Nalodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid antagonist, chemically related to naltrexone and naloxone. It is used in the treatment of opioid overdose and addiction.
Chemistry
Nalodeine is derived from thebaine, a naturally occurring opiate alkaloid found in the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum). It is synthesized by modifying thebaine's chemical structure to create a compound that blocks the effects of opioids rather than producing them.
Pharmacology
Nalodeine works by binding to the mu-opioid receptor in the brain, blocking the effects of opioids. This can reverse the effects of an opioid overdose, such as respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension. It can also help to prevent relapse in individuals recovering from opioid addiction by reducing the rewarding effects of opioids.
Clinical Use
Nalodeine is used in emergency situations to reverse the effects of opioid overdose. It can also be used as part of a comprehensive treatment program for opioid addiction, which may also include counseling and other behavioral therapies.
Side Effects
Possible side effects of nalodeine include nausea, vomiting, sweating, and increased heart rate. In rare cases, it can cause more serious side effects such as seizures, hallucinations, and severe allergic reactions.
See Also
References
<references />
-
Nalodeine
-
Nalodeine