Quinfamide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Quinfamide.svg|Quinfamide | |||
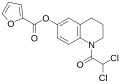
File:Quinfamide synthesis.svg|Quinfamide synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Quinfamide.svg|Quinfamide | File:Quinfamide.svg|Quinfamide | ||
File:Quinfamide synthesis.svg|Quinfamide synthesis | File:Quinfamide synthesis.svg|Quinfamide synthesis | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:38, 20 February 2025
Quinfamide is an antiparasitic agent used in the treatment of amebiasis, a parasitic infection caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It is particularly effective against the intestinal form of the disease.
Mechanism of Action
Quinfamide works by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of the Entamoeba histolytica parasite. It does this by interfering with the parasite's ability to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule that provides energy for many of the parasite's cellular processes.
Side Effects
Like all medications, Quinfamide can cause side effects. These may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In rare cases, it can cause more serious side effects such as allergic reactions and neurological disorders.
Dosage and Administration
Quinfamide is typically administered orally. The exact dosage will depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health status. It is important to follow the prescribing physician's instructions carefully to ensure the best possible outcome.
Precautions
Before starting treatment with Quinfamide, patients should inform their doctor about any other medications they are taking, as Quinfamide can interact with other drugs. It is also important to inform the doctor about any existing health conditions, as these can affect how the body responds to Quinfamide.