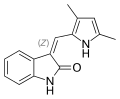Semaxanib: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Angiogenesis inhibitors]] | [[Category:Angiogenesis inhibitors]] | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Semaxanib.svg|Semaxanib | |||
File:Semaxanib synthesis.svg|Semaxanib synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:27, 20 February 2025
Semaxanib is a small molecule inhibitor that targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR). It is a synthetic compound that was developed as a potential treatment for various types of cancer. Semaxanib works by inhibiting the growth of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, which is crucial for the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Semaxanib, also known as SU5416, is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR-2, a key receptor involved in angiogenesis. By binding to this receptor, Semaxanib prevents the binding of VEGF, thereby inhibiting the signal for new blood vessel formation. This mechanism of action is thought to starve the cancer cells of the nutrients they need to grow and spread.
Clinical Trials[edit]
Semaxanib has been tested in several clinical trials for its efficacy in treating various types of cancer, including colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. However, the results have been mixed, with some studies showing a benefit and others showing no significant improvement over standard treatments.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all drugs, Semaxanib can cause side effects. The most common side effects reported in clinical trials include fatigue, nausea, and high blood pressure. More serious side effects can include bleeding, blood clots, and heart problems.
Current Status[edit]
As of now, Semaxanib is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the United States. However, research is ongoing to further understand its potential benefits and risks.
See Also[edit]
-
Semaxanib
-
Semaxanib synthesis