Serotonin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Serotonin == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Serotonin-2D-skeletal.svg|Serotonin 2D Skeletal Structure | |||
File:Pubmed equitativa hormonal.png|Pubmed Equitativa Hormonal | |||
File:Gray715.png|Gray's Anatomy Diagram | |||
File:Serotonin biosynthesis.svg|Serotonin Biosynthesis | |||
File:Biosynthesis and breakdown of serotonin and the catecholamines, and the metabolic block in AADC deficiency.png|Biosynthesis and Breakdown of Serotonin | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:22, 20 February 2025
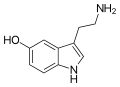
Serotonin (also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is a neurotransmitter that has a wide variety of functions in the human body. It is derived from tryptophan, an essential amino acid, and is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), blood platelets, and the central nervous system (CNS) of animals and humans.
Function[edit]
Serotonin is a crucial neurotransmitter that is involved in the regulation of several important bodily functions, including mood, appetite, sleep, and cognition. It also plays a role in the cardiovascular system, endocrine system, and musculoskeletal system.
Biosynthesis[edit]
Serotonin is synthesized from the essential amino acid tryptophan. This process occurs in two steps, both of which require specific enzymes. First, tryptophan is converted into 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) by the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase. Then, 5-HTP is converted into serotonin by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase.
Role in the body[edit]
In the gastrointestinal tract, serotonin regulates intestinal movements. In the blood platelets, it helps with blood clotting. In the central nervous system, serotonin is involved in regulating mood, appetite, sleep, and cognition.
Serotonin syndrome[edit]
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur if too much serotonin is present in the body. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including the use of certain drugs. Symptoms can range from mild (shivering and diarrhea) to severe (muscle rigidity, fever, and seizures).
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />