Menatetrenone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Nutritional supplements]] | [[Category:Nutritional supplements]] | ||
{{Vitamin-stub}} | {{Vitamin-stub}} | ||
== Menatetrenone == | |||
<gallery> | |||
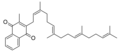
File:Menatetrenone.PNG|Menatetrenone | |||
File:Menatetrenone molecule spacefill.png|Menatetrenone molecule spacefill | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:21, 20 February 2025
Menatetrenone, also known as vitamin K2 or MK-4, is a type of Vitamin K that is involved in the modification of certain proteins, making them able to bind calcium ions. This process is essential for the proper functioning of the body, including bone formation and blood coagulation. Menatetrenone is synthesized by animal tissues and is also found in certain fermented foods.
Sources[edit]
Menatetrenone is primarily found in animal-based foods, such as meat, eggs, and dairy products. It is also present in high amounts in certain fermented foods, particularly Nattō, a traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans. Unlike its counterpart, Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone), which is found in green leafy vegetables, menatetrenone is not as widely available in the diet.
Biochemistry[edit]
Menatetrenone works by activating proteins that are involved in calcium metabolism. The most notable of these proteins are Osteocalcin, which is involved in bone formation, and Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), which inhibits calcification of arteries and cartilage. Menatetrenone achieves this by carboxylating specific glutamate residues on these proteins, a process that allows them to bind calcium ions.
Health Benefits[edit]
- Bone Health ###
Menatetrenone has been shown to play a significant role in maintaining bone health. It increases bone mineral density and reduces the risk of fractures, particularly in individuals with Osteoporosis. Its role in activating osteocalcin is particularly important for the incorporation of calcium into the bone matrix.
- Cardiovascular Health ###
By activating MGP, menatetrenone helps prevent the calcification of blood vessels and, therefore, may contribute to cardiovascular health. It has been suggested that higher intakes of vitamin K2 could be associated with a reduced risk of Coronary Heart Disease.
Clinical Use[edit]
Menatetrenone has been used in the treatment of osteoporosis in Japan. It is often prescribed alongside calcium and vitamin D supplements to enhance bone health and prevent fractures. There is also ongoing research into its potential benefits in preventing and treating other conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers.
Side Effects and Interactions[edit]
Menatetrenone is generally considered safe when consumed in amounts found in foods or as part of a balanced diet. However, when taken in high doses as a supplement, it may interact with anticoagulant medications, such as Warfarin, by antagonizing their effect. Patients on anticoagulant therapy should consult with a healthcare provider before taking menatetrenone supplements.
Conclusion[edit]
Menatetrenone is an important nutrient that plays a crucial role in bone and cardiovascular health. While it is not as widely recognized as other vitamins, its benefits in preventing and treating osteoporosis and potentially reducing the risk of coronary heart disease make it an important area of research and clinical interest.
This vitamin-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Menatetrenone[edit]
-
Menatetrenone
-
Menatetrenone molecule spacefill