Puberty: Difference between revisions
Replaced content with "File:YoungCoupleEmbracing-20070508.jpg|thumb|250px|Puberty is what happens to the bodies of girls and boys that changes them into women and men. When this happens, their..." Tag: Replaced |
CSV import |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category:Physiology]] | [[Category:Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:Human sexuality]] | [[Category:Human sexuality]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
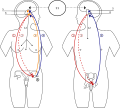
File:Hormons feedback - Sprzężenie zwrotne hormonow.svg|Puberty | |||
File:Male genitalia five Tanner stages.png|Puberty | |||
File:Adolescent Period Average boy 10 to 17 yo.jpg|Puberty | |||
File:Boy through puberty 11.3yo (prepuberal) 12.5yo, 14.9yo and 16.3yo (post puberal).jpg|Puberty | |||
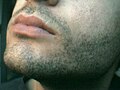
File:Stubbly face.jpg|Puberty | |||
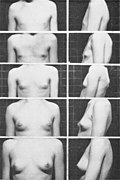
File:Female breasts five Tanner stages.jpg|Puberty | |||
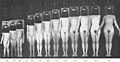
File:Adolescent Period Average girl 4 to 16 yo.jpg|Puberty | |||
File:Variations of the height of three boys from 12yo to the end of their growth spurt.jpg|Puberty | |||
File:Early and late maturing boys 11.5 to 16.6.jpg|Puberty | |||
File:Early and late maturing girls 8.0 to 14.5 yo.png|Puberty | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:21, 20 February 2025

Puberty is the period in human development during which physical growth and sexual maturation occur, marking the transition from childhood to adulthood. It is characterized by the development of secondary sexual characteristics, such as breast development in girls, growth of facial hair in boys, and changes in body composition in both sexes. Puberty is controlled by hormonal changes, primarily involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonads.
Stages of puberty[edit]
Puberty is typically divided into five Tanner stages, which describe the development of secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive maturity. The stages are as follows:
- Stage 1: Prepubertal – no signs of puberty
- Stage 2: Beginning of puberty – breast buds in girls, testicular enlargement in boys
- Stage 3: Continued development – growth of pubic hair, further breast development in girls, penis growth in boys
- Stage 4: Advanced puberty – appearance of underarm hair, adult-like breast development in girls, further penis and testicle growth in boys
- Stage 5: Adult – full sexual maturity
Timing of puberty[edit]
The onset of puberty varies between individuals and is influenced by genetic, environmental, and nutritional factors. In general, girls begin puberty between the ages of 8 and 13, while boys start between the ages of 9 and 14. Puberty typically lasts for 2-5 years.
Hormonal changes[edit]
The onset of puberty is triggered by the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus, which stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones then act on the gonads (ovaries in girls, testes in boys), leading to the production of sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone in girls, testosterone in boys) and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
[edit]
Several disorders can affect the normal progression of puberty, including:
- Precocious puberty – the early onset of puberty, before the age of 8 in girls or 9 in boys
- Delayed puberty – the absence of puberty by the age of 13 in girls or 14 in boys
- Hypogonadism – the underdevelopment or malfunction of the gonads, resulting in low sex hormone production and impaired sexual development
Treatment for these disorders may include hormone replacement therapy or medications to regulate hormone production.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>