Ro48-6791: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
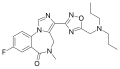
File:Ro48-6791.svg|Ro48-6791 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:13, 20 February 2025
Ro48-6791 is a benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1990s. It is a partial agonist at GABA_A receptors, which makes it less potent than other benzodiazepines, but still effective in treating anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
History[edit]
Ro48-6791 was first synthesized in the 1990s by the pharmaceutical company Hoffmann-La Roche. It was part of a series of new benzodiazepine derivatives that were designed to be safer and more effective than previous drugs in the class.
Pharmacology[edit]
Ro48-6791 is a partial agonist at GABA_A receptors, the same receptors targeted by other benzodiazepines. However, unlike full agonists, Ro48-6791 does not fully activate the receptor but instead, it only partially activates it. This results in a less potent, but still effective, drug.
Medical Uses[edit]
Ro48-6791 is primarily used in the treatment of anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Its lower potency makes it less likely to cause dependence and withdrawal symptoms compared to other benzodiazepines.
Side Effects[edit]
As with all benzodiazepines, Ro48-6791 can cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion. In rare cases, it can also cause more serious side effects like memory loss and depression.
See Also[edit]
-
Ro48-6791