Metencephalon: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:EmbryonicBrain.svg|Metencephalon | |||
File:Gray708.svg|Metencephalon | |||
File:Pons - Middle.svg|Metencephalon | |||
File:Pons - Inferior.svg|Metencephalon | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:02, 20 February 2025
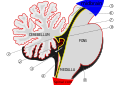
Metencephalon is a part of the developing vertebrate brain which is composed of the Pons and Cerebellum. It is formed from the Rhombencephalon, also known as the hindbrain, during the process of Embryogenesis.
Structure[edit]
The Metencephalon is one of the three primary vesicles that arise from the Neural tube. It is located between the Mesencephalon (midbrain) and the Myelencephalon (medulla oblongata). The Metencephalon develops into two structures: the Pons and the Cerebellum.
Pons[edit]
The Pons is a part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus. It serves several important functions in the brain, playing a role in motor control and sensory analysis. It is involved in controlling sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
Cerebellum[edit]
The Cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as in regulating fear and pleasure responses. Its movement-related functions are the most solidly established.
Development[edit]
During the process of Embryogenesis, the Metencephalon arises from the Rhombencephalon. The Rhombencephalon divides to form the Metencephalon and the Myelencephalon. The Metencephalon then further divides to form the Pons and the Cerebellum.
Function[edit]
The Metencephalon, being composed of the Pons and the Cerebellum, plays a crucial role in several functions in the body. It is involved in motor control, sensory analysis, and the regulation of several important bodily functions.