Blood compatibility testing: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Blood tests]] | [[Category:Blood tests]] | ||
[[Category:Immunohematology]] | [[Category:Immunohematology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Blood typing by manual tube method - type O positive.jpg|Blood typing by manual tube method - type O positive | |||
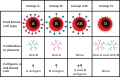
File:ABO blood type.svg|ABO blood type | |||
File:Kell and extended Rh antigen blood typing.jpg|Kell and extended Rh antigen blood typing | |||
File:Serology interpretation of antibody panel for blood group antigens.jpg|Serology interpretation of antibody panel for blood group antigens | |||
File:ANA begins process of blood typing soldiers 120324-N-JC271-021.jpg|ANA begins process of blood typing soldiers | |||
File:Bedside card.jpg|Bedside card | |||
File:Blood typing by gel card method (column agglutination or MTS gel) - type O positive.jpg|Blood typing by gel card method (column agglutination or MTS gel) - type O positive | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 20 February 2025
Blood compatibility testing is a critical process in transfusion medicine, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of blood transfusions. This testing is essential to match a donor's blood with that of a recipient to prevent adverse reactions, which can be life-threatening. Blood compatibility involves several key tests, including ABO blood grouping, Rh typing, antibody screening, and crossmatching.
ABO Blood Group System[edit]
The ABO blood group system is the primary blood group system in human blood transfusion. The four main blood types are A, B, AB, and O, which are determined by the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Compatibility within this system is crucial because the body can produce antibodies against foreign blood group antigens, leading to transfusion reactions.
Rh Factor[edit]
The Rh factor is another significant antigen in blood transfusion. It is categorized into Rh positive and Rh negative, depending on the presence or absence of the D antigen on the surface of red blood cells. Rh compatibility is especially important in pregnancy and blood transfusion to prevent Rh disease of the newborn and transfusion reactions.
Antibody Screening[edit]
Antibody screening is a test performed to detect unexpected antibodies in the recipient's serum that could react with antigens on the donor's red blood cells. This step is crucial for identifying individuals who may require blood from specially selected donors to avoid hemolytic transfusion reactions.
Crossmatching[edit]
Crossmatching is the final step in blood compatibility testing. This test involves mixing a small sample of the recipient's serum with the donor's red blood cells to check for any adverse reactions. A positive crossmatch indicates that the donor's blood is incompatible with the recipient's, while a negative crossmatch indicates compatibility.
Importance of Blood Compatibility Testing[edit]
Blood compatibility testing is vital for preventing transfusion-related complications, such as hemolytic reactions, alloimmunization, and transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). It ensures that recipients receive the most compatible blood, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions and improving transfusion outcomes.
Conclusion[edit]
Blood compatibility testing is a complex but essential process in transfusion medicine, involving multiple tests to ensure the safe and effective matching of donor and recipient blood. Through the ABO and Rh systems, antibody screening, and crossmatching, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the risks associated with blood transfusions, ensuring patient safety and well-being.
-
Blood typing by manual tube method - type O positive
-
ABO blood type
-
Kell and extended Rh antigen blood typing
-
Serology interpretation of antibody panel for blood group antigens
-
ANA begins process of blood typing soldiers
-
Bedside card
-
Blood typing by gel card method (column agglutination or MTS gel) - type O positive