Betahistine: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Betahistine.svg|Betahistine | |||
File:Betahistine ball-and-stick.png|Betahistine ball-and-stick model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 20 February 2025
Betahistine is a medication that is primarily used to treat vertigo and Meniere's disease. It is a type of histamine analogue medicine that works by improving blood flow in the inner ear, which reduces the build-up of pressure. This, in turn, reduces the severity and frequency of vertigo attacks and other symptoms of Meniere's disease.
Etymology[edit]
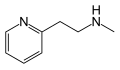
The term "Betahistine" is derived from its chemical name, 2-(2-pyridyl)ethylamine, which is a derivative of histamine.
Medical Uses[edit]
Betahistine is used to treat a variety of conditions related to the inner ear. These include:
- Vertigo: Betahistine is often prescribed to help manage symptoms of vertigo, such as dizziness, nausea, and problems with balance.
- Meniere's disease: This is a chronic condition characterized by recurrent vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Betahistine helps to reduce the frequency and severity of these symptoms.
- Tinnitus: While not a primary treatment for tinnitus, Betahistine can help to alleviate some of the symptoms in conjunction with other treatments.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all medications, Betahistine can cause side effects. These may include:
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if these or any other side effects occur.