Imine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Chemical reactions]] | [[Category:Chemical reactions]] | ||
[[Category:Biochemistry]] | [[Category:Biochemistry]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Imine_general_structure_B.svg|Imine | |||
File:Aldimine-(primary)-skeletal.svg|Aldimine (primary) | |||
File:Aldimine-(secondary)-skeletal.svg|Aldimine (secondary) | |||
File:Imine-(primary)-skeletal.svg|Imine (primary) | |||
File:Imine-(secondary)-skeletal.svg|Imine (secondary) | |||
File:Imine-synthesis.svg|Imine synthesis | |||
File:Hexafluoroacetone_imine.svg|Hexafluoroacetone imine | |||
File:Mannich.png|Mannich | |||
File:ImineReduction.svg|Imine reduction | |||
File:PLP_mechanism.svg|PLP mechanism | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:11, 18 February 2025
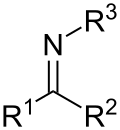
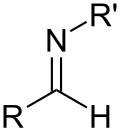
Imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen (H) or an organic group (R). If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound can sometimes be referred to as a Schiff base. The carbon atom has two additional single bonds.
Structure and classification of imines[edit]
Imines are similar to ketones and aldehydes in that they contain a C=O bond. The difference is that imines contain a C=N bond instead. The C=N bond gives imines their unique properties and reactivity.
Imines can be classified into two types:
- Primary imines: have the general formula RCH=NR'
- Secondary imines: have the general formula R2C=NR' (where R' ≠ H)
Preparation of imines[edit]
Imines are typically prepared by the condensation of primary amines and aldehydes, in a process known as imine formation. The reaction is acid-catalyzed and proceeds via the formation of a carbinolamine intermediate.
Reactions of imines[edit]
Imines are susceptible to hydrolysis to give back the starting amine and aldehyde. This process is called imine hydrolysis. Imines can also react with Grignard reagents, organolithium reagents, and hydride reagents to give amines.
Biological importance of imines[edit]
In biological systems, imines can be found in a variety of important reactions. For example, in the biosynthesis of alkaloids, imines serve as intermediates. Imines are also involved in the Mannich reaction, which is a key step in the biosynthesis of many natural products.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />