Obesity-associated morbidity: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
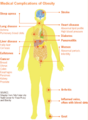
File:Medical_complications_of_obesity.png|Medical complications of obesity | |||
File:Death-rate-from-obesity.svg|Death rate from obesity | |||
File:Blausen_0463_HeartAttack.png|Heart attack illustration | |||
File:Adipomastia_001.jpg|Adipomastia | |||
File:MCA_Territory_Infarct.svg|MCA Territory Infarct | |||
File:Hepatocellular_carcinoma_1.jpg|Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
File:Relationship_between_bmi_and_suicide.png|Relationship between BMI and suicide | |||
File:Cpap-example.jpg|CPAP example | |||
File:Gout2010.JPG|Gout | |||
File:Urinary_system_00000.gif|Urinary system | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:10, 18 February 2025
Obesity-associated morbidity refers to the health complications and diseases that are associated with obesity. Obesity is a medical condition characterized by an excess of body fat, which can have a negative impact on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and increased health problems.
Overview
Obesity is a complex disorder involving an excessive amount of body fat. It's not just a cosmetic concern. It is a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.
Causes
There are many reasons why someone might become obese. Some of the most common causes include:
- Consuming more calories than are burned through exercise and normal daily activities
- Having an inactive lifestyle
- Lack of sleep
- Certain medications
- Genetics, which can affect how your body processes food into energy and how fat is stored
Health Risks
Obesity can lead to a number of serious and potentially life-threatening conditions, including:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Cancer
- Sleep apnea
- Osteoarthritis
- Fatty liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Pregnancy complications
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing obesity and treating those who are obese is a public health priority. Some of the most effective methods for preventing and treating obesity include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet
- Regular physical activity
- Limiting sedentary activities
- Getting enough sleep
- Stress management