Phakomatosis: Difference between revisions
m 1 revision imported |
CSV import |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
{{nervoussystem-disease-stub}} | {{nervoussystem-disease-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
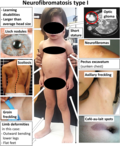
File:Symptoms_of_neurofibromatosis_type_1_-_censored_version.png|Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 | |||
File:Symptoms_of_neurofibromatosis_type_1.png|Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 | |||
File:Diagnostic_criteria_of_neurofibromatosis_type_I.jpg|Diagnostic Criteria of Neurofibromatosis Type I | |||
File:Neurofibromatosis_type_II_tumor_types.png|Neurofibromatosis Type II Tumor Types | |||
File:Patient_with_facial_angiofibromas_caused_by_tuberous_sclerosis.jpg|Patient with Facial Angiofibromas Caused by Tuberous Sclerosis | |||
File:Symptoms_and_signs_of_tuberous_sclerosis.png|Symptoms and Signs of Tuberous Sclerosis | |||
File:Port_wine_stains_of_an_8-year-old_female_with_Sturge-Weber_Syndrome.png|Port Wine Stains of an 8-year-old Female with Sturge-Weber Syndrome | |||
File:Cysts_and_tumors_in_Von_Hippel–Lindau_disease.png|Cysts and Tumors in Von Hippel–Lindau Disease | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:52, 18 February 2025
| Phakomatoses | |
|---|---|
| [[File:|250px|alt=|]] | |
| Synonyms | Phakomatosis |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | |
| Symptoms | |
| Complications | |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | |
| Deaths | |
Phakomatoses refers to a group of neuro-oculo-cutaneous syndromes or neurocutaneous disorders involving structures arising from the embryonic ectoderm. These multisystem disorders involve the ectodermal structures like central nervous system, skin and eyes.<ref name="neuroderm 2014">,
Neurodermatology., Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 121, pp. 1561–94, DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-7020-4088-7.00104-8, PMID: 24365436,</ref> The lesions have a variable severity.<ref name="Rook(FRCP.)2004">, Rook's textbook of dermatology. online version, Wiley-Blackwell, 2004, ISBN 978-0-632-06429-8, Pages: 5–,</ref><ref>, Neurocutaneous disorders., Dermatologic Clinics, Vol. 20(Issue: 3), pp. 547–60, viii, DOI: 10.1016/s0733-8635(02)00005-0, PMID: 12170887,</ref> However, it has been subsequently noted that mesodermal and endodermal tissues too are involved.
A number of genetic and acquired diseases come in this category and may affect one or more of these tissues. However, in some conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau disease, ectodermal presentation is minimal.<ref>
Phakomatosis(link). {{{website}}}. GE.
</ref>
Examples
Phakomatoses are inconsistently defined, and there is a lack of consensus about what conditions are included in this category.<ref name="YanoffDuker2009">,
Ophthalmology. online version, Elsevier Health Sciences, 2009, ISBN 978-0-323-04332-8, Pages: 937–,</ref>
Conditions included are:
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Incontinentia pigmenti
- Neurofibromatosis
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Wyburn-Mason syndrome (Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome)
- von Hippel-Lindau disease
Etymology
The term, from the Greek φακός, phakos, "spot, lens", suffix-(o)ma (-ωμα) and the suffix -osis, also called "Mother's spot" or "Birth mark" was introduced by Jan van der Hoeve in 1920, before the distinct genetic basis of each of these diseases was understood.<ref> Enersen, Ole Daniel. Jan van der Hoeve(link). {{{website}}}. Who Named It?.
</ref>
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External links
- OMIM is an Online Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders
| Phakomatosis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1
-
Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1
-
Diagnostic Criteria of Neurofibromatosis Type I
-
Neurofibromatosis Type II Tumor Types
-
Patient with Facial Angiofibromas Caused by Tuberous Sclerosis
-
Symptoms and Signs of Tuberous Sclerosis
-
Port Wine Stains of an 8-year-old Female with Sturge-Weber Syndrome
-
Cysts and Tumors in Von Hippel–Lindau Disease