Craniosynostosis: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cranialsynostosis.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Single_suture_synostosis.png|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Плагиоцефалия.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Anterior_plagiocephaly_right_frontal_and_top_view_2.png|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Précis_de_psychiatrie_3.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Carpenter_Syndrome_1.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Patient_with_Crouzon_syndrome_(1912).jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Osseous_Deformity_Case_1.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Girl_aged_17_years_with_marked_proptosis_Wellcome_L0062481.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Pyrgocephalus.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Suturefusion2.jpg|Craniosynostosis | |||
File:Sobo_1909_105.png|Craniosynostosis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:50, 18 February 2025
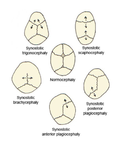
Craniosynostosis is a medical condition in which the skull bones of an infant close prematurely, before the brain is fully formed. This can lead to abnormal growth patterns of the skull and can affect the shape of the head and face.
Causes
Craniosynostosis is usually caused by a genetic mutation. It can be associated with certain genetic syndromes, such as Crouzon syndrome, Apert syndrome, and Pfeiffer syndrome. However, in many cases, the cause of craniosynostosis is unknown.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of craniosynostosis is an abnormally shaped head. Other symptoms can include developmental delays, difficulty feeding, and increased intracranial pressure. In severe cases, craniosynostosis can lead to vision problems, sleep apnea, and other serious health issues.
Diagnosis
Craniosynostosis is usually diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans. Genetic testing may also be performed to determine if the condition is associated with a genetic syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment for craniosynostosis usually involves surgery to separate the fused skull bones. This allows the brain to grow normally. In some cases, a helmet may be used after surgery to help shape the skull. Other treatments may include physical therapy and special education services to help with developmental delays.