Aspergillus fumigatus: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Pathogenic fungi]] | [[Category:Pathogenic fungi]] | ||
{{Fungi-stub}} | {{Fungi-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Aspergillus.jpg|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:Aspergillus_fumigatus_Invasive_Disease_Mechanism_Diagram.jpg|Invasive Disease Mechanism Diagram | |||
File:Journal.ppat.0030128.g001.png|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:Secondary_metabolite_regulation_by_LaeA.jpg|Secondary Metabolite Regulation by LaeA | |||
File:Aspergillus_fumigatus_01.jpg|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:Conidia_phialoconidia_of_Aspergillus_fumigatus_PHIL_300_lores.jpg|Conidia phialoconidia of Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:070522-aspergillus_009.jpg|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:Aspergillus_fumigatus.jpg|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
File:10523_Aspergillus_fumigatus.jpg|Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 18 February 2025
Aspergillus fumigatus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus, and is one of the most common Aspergillus species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency.
Taxonomy[edit]
Aspergillus fumigatus was first described by the German mycologist Friedrich Wilhelm Gottlieb Rostkovius in 1808. It is a member of the genus Aspergillus, which includes over 200 species.
Morphology[edit]
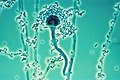
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprophytic fungus that plays a major role in recycling environmental carbon and nitrogen. Its spores are ubiquitous in the atmosphere and are commonly inhaled, though they rarely cause disease in healthy individuals.
Pathogenicity[edit]
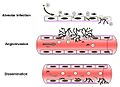
Aspergillus fumigatus is an opportunistic pathogen and can cause a variety of diseases in humans, the most common of which is invasive aspergillosis. This disease primarily affects individuals with a compromised immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS, those undergoing chemotherapy, or organ transplant recipients.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for diseases caused by Aspergillus fumigatus typically involves antifungal medications. The choice of medication can depend on a variety of factors, including the specific disease, the patient's overall health, and the patient's response to treatment.
See also[edit]
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Invasive Disease Mechanism Diagram
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
-
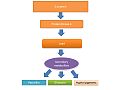
Secondary Metabolite Regulation by LaeA
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Conidia phialoconidia of Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Aspergillus fumigatus