Estradiol benzoate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Endocrinology-stub}} | {{Endocrinology-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Estradiol.svg|Estradiol_benzoate | |||
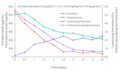
File:Hormone_levels_with_twice-daily_injectable_estradiol_benzoate_in_transgender_women.png|Hormone levels with twice-daily injectable estradiol benzoate in transgender women | |||
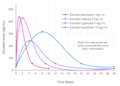
File:Estradiol_levels_after_single_intramuscular_injections_of_different_doses_of_estradiol_benzoate_in_premenopausal_women.png|Estradiol levels after single intramuscular injections of different doses of estradiol benzoate in premenopausal women | |||
File:Estradiol_levels_after_a_single_5_mg_intramuscular_injection_of_estradiol_esters.png|Estradiol levels after a single 5 mg intramuscular injection of estradiol esters | |||
File:Estradiol_levels_after_injections_of_estradiol,_estradiol_benzoate,_estradiol_valerate,_and_estradiol_undecylate_in_women.png|Estradiol levels after injections of estradiol, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerate, and estradiol undecylate in women | |||
File:Idealized_curves_of_estradiol_levels_after_injection_of_different_estradiol_esters_in_women.png|Idealized curves of estradiol levels after injection of different estradiol esters in women | |||
File:Vaginal_cornification_with_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_different_estradiol_esters_in_women.png|Vaginal cornification with a single intramuscular injection of different estradiol esters in women | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:36, 18 February 2025
Estradiol benzoate (EB), a synthetic form of estrogen, is an estrogen ester specifically, the 3-benzoate ester of estradiol. It is used in HRT for menopausal symptoms and in contraceptive pills. It is also employed in veterinary medicine as a component of hormonal veterinary products.
Medical Uses
Estradiol benzoate is used primarily in HRT for treating signs of menopause such as hot flashes and vaginal atrophy. It is also used in hormonal therapy for transgender women as part of the feminizing hormone therapy. In veterinary medicine, it is used to stimulate estrus in animals.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Estradiol benzoate, like estradiol, binds to and activates the estrogen receptor. Its estrogenic activity is responsible for the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues and secondary sexual characteristics. It also has important effects on bone density, liver metabolism, and mental health.
Pharmacokinetics
After administration, estradiol benzoate is slowly absorbed and hydrolyzed into estradiol, the active form, and benzoic acid. The conversion allows for a more prolonged duration of action compared to estradiol itself, making it suitable for less frequent dosing schedules in therapeutic applications.
Adverse Effects
The adverse effects of estradiol benzoate are similar to those of estradiol and other estrogens. These can include nausea, breast tenderness, headache, and an increased risk of thromboembolic events and certain types of cancers such as breast cancer. Monitoring and evaluation by a healthcare provider are essential to mitigate these risks.
Chemistry
Estradiol benzoate is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a derivative of estradiol. It is more lipophilic than estradiol due to the benzoate ester, which affects its pharmacokinetics, including absorption and half-life.
History
Estradiol benzoate was one of the first estrogen esters to be discovered and used medically. It has been available for medical use since the 1930s, making it one of the earliest forms of estrogen therapy available.
Society and Culture
Legal status and availability of estradiol benzoate can vary by country. It remains an important component of hormone therapy regimens, despite the development of newer estrogen compounds and formulations.

This article is a endocrinology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Estradiol_benzoate
-
Hormone levels with twice-daily injectable estradiol benzoate in transgender women
-
Estradiol levels after single intramuscular injections of different doses of estradiol benzoate in premenopausal women
-
Estradiol levels after a single 5 mg intramuscular injection of estradiol esters
-
Estradiol levels after injections of estradiol, estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerate, and estradiol undecylate in women
-
Idealized curves of estradiol levels after injection of different estradiol esters in women
-
Vaginal cornification with a single intramuscular injection of different estradiol esters in women