Atmospheric dispersion modeling: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{environment-stub}} | {{environment-stub}} | ||
{{math-stub}} | {{math-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:AirPollutionSource.jpg|Air pollution source | |||
File:Gaussian_Plume_(SVG).svg|Gaussian plume model | |||
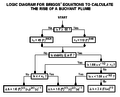
File:BriggsLogic.png|Briggs logic for dispersion | |||
File:Résultat_de_modélisation_de_dispersion_atmosphérique_-_Avizo_Experts-Conseils.png|Atmospheric dispersion modeling result | |||
File:HYSPLITTrajectoriesforNewportStateParkpage72.jpg|HYSPLIT trajectories for Newport State Park | |||
File:Vanadis_a1_test.gif|Atmospheric dispersion modeling | |||
File:Vanadis_a2_test.gif|Atmospheric dispersion modeling | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 18 February 2025
Atmospheric dispersion modeling is the mathematical simulation of how air pollutants disperse in the atmosphere. It is performed with computer programs that solve the mathematical equations and algorithms which simulate the pollutant dispersion. The dispersion models are used to estimate or to predict the downwind concentration of air pollutants or toxins emitted from sources such as industrial plants, vehicular traffic or accidental chemical releases.
Overview[edit]
Atmospheric dispersion models are important in the field of air quality and environmental compliance. They are typically used to determine the impact of pollutants emitted into the atmosphere. The models can also be used to predict future concentrations in time and space under specific scenarios. Thus, they are an essential tool in the environmental impact assessment of industrial projects.
Types of Models[edit]
There are several types of atmospheric dispersion models, including Gaussian models, Lagrangian models, Eulerian models, and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models.
Gaussian models, also known as plume dispersion models, are the simplest type of dispersion model and are typically used for short range predictions up to about 25 kilometers.
Lagrangian models are more complex and can model pollutant dispersion over larger areas and over longer periods of time. They are typically used for long range dispersion modeling and for modeling of pollutants that transform in the atmosphere.
Eulerian models are the most complex type of dispersion model and are typically used for regional and global scale dispersion modeling. They can also model the interaction of different pollutants in the atmosphere.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models are used for detailed investigations of pollutant dispersion at small scales, such as around buildings or complex terrain.
Applications[edit]
Atmospheric dispersion models are used in a wide range of applications, including air quality management, emergency response planning, and environmental impact assessments. They are also used in the design and operation of industrial facilities to ensure compliance with air quality standards and regulations.
See Also[edit]
- Air pollution dispersion terminology
- Air quality index
- Air Quality Modeling Group
- Air Resources Laboratory
- List of atmospheric dispersion models
- UK Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling Liaison Committee

This article is a environment-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!

This article is a mathematics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Air pollution source
-
Gaussian plume model
-
Briggs logic for dispersion
-
Atmospheric dispersion modeling result
-
HYSPLIT trajectories for Newport State Park
-
Atmospheric dispersion modeling
-
Atmospheric dispersion modeling