Heredity: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Jug_Ear_Heredity.jpg|Heredity | |||
File:DNA_animation.gif|DNA Animation | |||
File:Aristotle's_model_of_Inheritance.png|Aristotle's Model of Inheritance | |||
File:Independent_assortment_&_segregation.svg|Independent Assortment & Segregation | |||
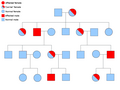
File:Autosomal_dominant.png|Autosomal Dominant | |||
File:Autosomal_recessive.png|Autosomal Recessive | |||
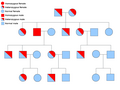
File:Sex_linked_inheritance.png|Sex-linked Inheritance | |||
File:Autosomal_recessive_inheritance_for_affected_enzyme.png|Autosomal Recessive Inheritance for Affected Enzyme | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:20, 18 February 2025
Heredity is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics.
Overview[edit]
In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype.
The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin comes from the interaction between a person's phenotype and sunlight; thus, suntans are not passed on to people's children. However, some people tan more easily than others, due to differences in their genotype: a striking example of the interaction between genotype and environment.
Genes and inheritance[edit]
In asexual organisms, genes are inherited together, or linked, as they cannot mix with genes of other organisms during reproduction. In contrast, the offspring of sexual organisms contains a mixture of their parents' genes. A number of mechanisms of recombination such as chromosomal crossover (crossing over) during meiosis and mutation can alter the genotype of the offspring.
Genetic disorders[edit]
Certain genetic disorders can be inherited from the parents, while other genetic diseases are caused by acquired changes or mutations in a preexisting gene or group of genes. Mutations can occur either randomly or due to some environmental exposure.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />