Organ of Corti: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Ear-stub}} | {{Ear-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
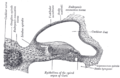
File:Cochlea-crosssection.svg|Cross-section of the cochlea | |||
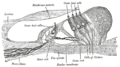
File:Organ_of_corti.svg|Diagram of the Organ of Corti | |||
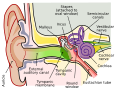
File:Anatomy_of_the_Human_Ear.svg|Anatomy of the human ear | |||
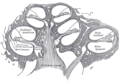
File:Gray903.png|Organ of Corti | |||
File:Gray928.png|Organ of Corti | |||
File:Gray929.png|Organ of Corti | |||
File:Gray930.png|Organ of Corti | |||
File:Gray931.png|Organ of Corti | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:16, 18 February 2025
Organ of Corti
The Organ of Corti is a structure located in the cochlea of the inner ear and is named after the Italian anatomist Alfonso Corti, who first described it. It is the main sensory organ of the auditory system and plays a crucial role in the process of hearing.
Structure[edit]
The Organ of Corti is situated on the basilar membrane of the cochlea, which is coiled up in the inner ear. It consists of several types of cells, including hair cells, supporting cells, and nerve cells. The hair cells are the sensory cells that convert the mechanical vibrations of sound waves into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Organ of Corti is to convert the mechanical energy of sound waves into electrical energy that can be interpreted by the brain. This process, known as mechanotransduction, involves the movement of the hair cells in response to the vibrations of the basilar membrane. As the hair cells move, they open ion channels that allow ions to flow into the cells, creating an electrical signal.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the Organ of Corti can result in sensorineural hearing loss, which is a type of hearing loss caused by damage to the hair cells or the auditory nerve. This can be caused by exposure to loud noise, aging, certain medications, and some genetic conditions. Treatment options for sensorineural hearing loss include hearing aids and cochlear implants.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Cross-section of the cochlea
-
Diagram of the Organ of Corti
-
Anatomy of the human ear
-
Organ of Corti
-
Organ of Corti
-
Organ of Corti
-
Organ of Corti
-
Organ of Corti