Glossoepiglottic folds: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray953.png|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide8ttt.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide10ttt.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide3uuu.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide14uuu.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide1kuku.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
File:Slide3kuku.JPG|Glossoepiglottic folds | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:13, 18 February 2025
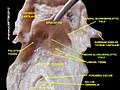
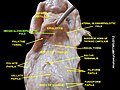
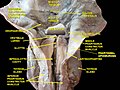
Glossoepiglottic Folds are anatomical structures found in the human body, specifically in the throat region. They are part of the larynx and play a crucial role in the process of swallowing.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Glossoepiglottic" is derived from two Greek words: "glossa," meaning tongue, and "epiglottis," which refers to the leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food from entering the windpipe.
Anatomy[edit]
The Glossoepiglottic Folds are divided into two types: the median glossoepiglottic fold and the lateral glossoepiglottic fold. The median glossoepiglottic fold is a small, midline fold of mucous membrane that extends from the base of the tongue to the epiglottis. The lateral glossoepiglottic fold, on the other hand, extends from the side of the tongue to the lateral margin of the epiglottis.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Glossoepiglottic Folds is to aid in the process of swallowing. They help guide food and liquid from the mouth into the esophagus, preventing it from entering the windpipe and causing choking.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Abnormalities or injuries to the Glossoepiglottic Folds can lead to difficulties in swallowing, also known as dysphagia. This can result from various conditions, including neurological disorders, muscular disorders, or structural abnormalities in the throat.