Lewy body: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Lewy_bodies_(alpha_synuclein_inclusions).svg|Lewy bodies (alpha synuclein inclusions) | |||
File:Lewy_Koerperchen.JPG|Lewy Koerperchen | |||
File:Dorsal_motor_nucleus_of_Vagus_with_Lewy_body_pathology_(alpha_synucleinopathy).svg|Dorsal motor nucleus of Vagus with Lewy body pathology (alpha synucleinopathy) | |||
File:Lewy_neurites_alpha_synuclein.jpg|Lewy neurites alpha synuclein | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:06, 18 February 2025
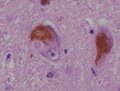
Lewy body is a type of protein deposit found in the brain of patients with certain neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. These deposits are named after the neurologist Friedrich Heinrich Lewy, who first described them.
Overview[edit]
Lewy bodies are abnormal aggregates of protein that develop inside nerve cells, contributing to Parkinson's disease, Dementia with Lewy bodies, and some other disorders. They are identified by their particular shape and protein content.
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of Lewy body formation is unknown. However, they are thought to be associated with the degeneration of nerve cells, which is a characteristic of Parkinson's disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies.
Symptoms[edit]
The presence of Lewy bodies in the brain can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of Lewy body disease can be challenging, as its symptoms often overlap with those of other conditions, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. However, certain clinical features, such as visual hallucinations and fluctuations in cognitive function, can suggest the presence of Lewy bodies.
Treatment[edit]
There is currently no cure for diseases associated with Lewy bodies. However, treatments can help manage symptoms. These may include medications for motor symptoms, cognitive symptoms, and psychiatric symptoms.