Danishefsky's diene: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category:Name reactions]] | [[Category:Name reactions]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Danishefsky-Diene_Structural_Formulae.png|Danishefsky's diene structural formulae | |||
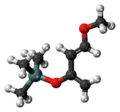
File:Danishefsky's_diene_3D_ball.png|Danishefsky's diene 3D ball model | |||
File:Danishefskys_diene_application2.png|Application of Danishefsky's diene | |||
File:AzaDA_DanishefskyDiene.png|AzaDA Danishefsky diene | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:04, 18 February 2025
Danishefsky's diene is a type of organic compound that is used in organic chemistry as a diene in Diels-Alder reactions. It was first synthesized by Samuel J. Danishefsky, a renowned American chemist, and hence, it bears his name.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Danishefsky's diene" is derived from the name of its discoverer, Samuel J. Danishefsky, and the term "diene", which is a type of organic compound that contains two alternating double bonds.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Danishefsky's diene is a cyclohexadiene derivative. It has a molecular formula of C9H10O2 and a molecular weight of 150.18 g/mol. The compound is characterized by its unique structure, which consists of a six-membered ring with two double bonds and an ester group attached to it.
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis of Danishefsky's diene involves the reaction of dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate with isopropylidene malonate in the presence of a base. The reaction proceeds via a Michael addition followed by an aldol condensation.
Applications[edit]
Danishefsky's diene is primarily used in Diels-Alder reactions. It acts as a diene, reacting with various dienophiles to form six-membered rings. The resulting products are often used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, including natural products and pharmaceuticals.
Related Terms[edit]
- Diels-Alder reaction: A chemical reaction between a diene and a dienophile, resulting in a six-membered ring.
- Diene: An organic compound that contains two alternating double bonds.
- Dienophile: A compound that can react with a diene in a Diels-Alder reaction.
- Michael addition: A reaction where a nucleophile adds to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
- Aldol condensation: A reaction where an enol or enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone, followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.