MCPA: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
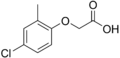
File:MCPA_structure.png|MCPA | |||
File:MCPA_use_in_the_USA_in_2017.png|MCPA use in the USA in 2017 | |||
File:Bio-degradation_of_MCPA.png|Bio-degradation of MCPA | |||
File:Oxidation_of_MCPA_by_hydroxyl_radicals.png|Oxidation of MCPA by hydroxyl radicals | |||
File:Oxidation_of_MCPA_by_positive_holes_h+.png|Oxidation of MCPA by positive holes (h+) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:58, 18 February 2025
MCPA is a powerful, selective, widely used phenoxy herbicide that is particularly effective against broadleaf weeds. It is structurally similar to 2,4-D, another commonly used herbicide, and both are often compared due to their similar modes of action. MCPA is used in agriculture, horticulture, and turf management.
History[edit]
MCPA was first introduced in the 1940s, making it one of the oldest herbicides still in use today. It was developed as a cheaper alternative to 2,4-D and has since become a staple in weed control.
Uses[edit]
MCPA is primarily used to control broadleaf weeds in cereal crops, pastures, and turf. It is also used in the control of aquatic weeds. MCPA is often used in combination with other herbicides to increase its effectiveness.
Mode of Action[edit]
MCPA works by mimicking the natural plant hormone auxin, causing uncontrolled growth and eventually death in susceptible plants. It is absorbed through the leaves and is translocated to the growth points of the plant.
Environmental Impact[edit]
MCPA is moderately toxic to birds and mammals, and slightly toxic to fish and aquatic invertebrates. It is not expected to bioaccumulate. MCPA can leach into groundwater and may cause harm to non-target plants.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to MCPA can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Long-term exposure can lead to more serious health effects such as damage to the liver and kidneys.
Regulation[edit]
In many countries, the use of MCPA is regulated due to its potential environmental and health impacts. In the European Union, for example, MCPA is approved for use but with restrictions.