Personality: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Personality == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Wiki-grafik_peats-de_big_five_ENG.svg|Diagram of the Big Five personality traits | |||
File:Wm_james.jpg|William James, American philosopher and psychologist | |||
File:Locke-John-LOC.jpg|John Locke, English philosopher | |||
File:Benedictus_(Baruch)_Spinoza_(anoniem_schilderij,_Gemeentemuseum_Den_Haag),_Bestanddeelnr_935-0843.jpg|Baruch Spinoza, Dutch philosopher | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:48, 18 February 2025
Personality refers to the unique set of characteristics, traits, behaviors, and patterns that define an individual and differentiate them from others. These traits may include attitudes, habits, psychological traits, personal beliefs, intelligence, and others. Personality is believed to be influenced by various factors, including genetic, environmental, and developmental factors.
Overview[edit]
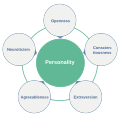
Personality is often described in terms of trait patterns, which are consistent patterns of thought, feeling, and behavior. These traits are often categorized into five broad dimensions, known as the Big Five, which include openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Development of Personality[edit]
The development of personality is influenced by both nature and nurture. Genetic factors contribute to the basic foundation of personality, including temperament and disposition. Environmental factors, such as upbringing, culture, and life experiences, further shape these basic traits into the unique personality of an individual.
Personality Assessment[edit]
Personality can be assessed through various methods, including personality tests, behavioral observations, and clinical interviews. These assessments can provide valuable insights into an individual's behavior, skills, and potential for certain roles or treatments.
Personality Disorders[edit]
Personality disorders are a category of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience. These patterns deviate markedly from the expectations of the individual's culture and lead to significant distress or impairment.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />