Elaeis guineensis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{agriculture-stub}} | {{agriculture-stub}} | ||
{{environment-stub}} | {{environment-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Elaeis_guineensis_-_Köhler–s_Medizinal-Pflanzen-056.jpg|Elaeis guineensis illustration from Köhler's Medicinal Plants | |||
File:Elaeis_guineensis_fruits_on_tree.jpg|Elaeis guineensis fruits on tree | |||
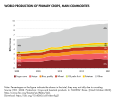
File:World_Production_Of_Primary_Crops,_Main_Commodities.svg|World production of primary crops, main commodities | |||
File:Fruit_oil_palm.JPG|Fruit of oil palm | |||
File:Production_Of_Oil_Palm_Fruit_(2021).svg|Production of oil palm fruit (2021) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 18 February 2025
Elaeis guineensis, also known as the African oil palm, is a species of palm native to West Africa, specifically the area between Angola and Gambia. It is a principal source of palm oil, a versatile vegetable oil used in a variety of applications, from cooking to cosmetics and biofuel.
Description[edit]
The Elaeis guineensis tree is a single-stemmed palm that grows up to 20 meters tall. It has large, pinnate leaves that can reach 5 meters in length. The tree produces dense clusters of fruit, known as palm fruit, which contain a high percentage of oil.
Cultivation and Production[edit]
Elaeis guineensis is primarily grown in tropical climates where rainfall is abundant. The tree begins to bear fruit after 3-4 years and reaches peak production around 10 years. The fruit is harvested manually and then processed to extract the palm oil.
The global demand for palm oil has led to the expansion of Elaeis guineensis cultivation, particularly in Southeast Asia. However, this expansion has raised environmental concerns due to deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
Uses[edit]
The primary use of Elaeis guineensis is the production of palm oil. This oil is used in a wide range of products, including food, cosmetics, and biofuel. The tree's other parts, such as the leaves and trunk, can also be used for various purposes, including construction and fiber production.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The cultivation of Elaeis guineensis has significant environmental implications. Large-scale deforestation to make way for palm oil plantations has led to habitat loss for many species, including the orangutan and Sumatran tiger. It also contributes to climate change due to the release of carbon dioxide when forests are cleared.
See Also[edit]

This article is a agriculture stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!

This article is a environment-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Elaeis guineensis illustration from Köhler's Medicinal Plants
-
Elaeis guineensis fruits on tree
-
World production of primary crops, main commodities
-
Fruit of oil palm
-
Production of oil palm fruit (2021)