Urinothorax: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Respiratory diseases]] | [[Category:Respiratory diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Urological conditions]] | [[Category:Urological conditions]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
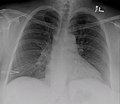
File:Pleural_effusion_caused_by_urinothorax.png|Pleural effusion caused by urinothorax | |||
File:CT_scan_showing_placement_of_the_nephrostomy_tube_in_a_case_of_urinothorax_being_treated.jpg|CT scan showing placement of the nephrostomy tube in a case of urinothorax being treated | |||
File:Cureus-0011-00000004559-i03.jpg|Urinothorax | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 04:25, 18 February 2025
Urinothorax
Urinothorax is a rare medical condition characterized by the accumulation of urine in the pleural cavity, the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This condition is a type of pleural effusion, which is the build-up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs.
Causes
Urinothorax typically occurs due to a disruption in the urinary tract, which allows urine to leak into the pleural space. Common causes include:
- Trauma to the urinary system, such as from an accident or surgical procedure.
- Obstructive uropathy, where a blockage in the urinary tract leads to increased pressure and rupture.
- Nephrostomy tube placement complications.
- Renal or ureteral injury.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of urinothorax involves the leakage of urine from the urinary tract into the retroperitoneal space, which then tracks into the pleural cavity. This can occur due to a pressure gradient or direct communication between the urinary system and the pleural space.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of urinothorax is challenging due to its rarity and the non-specific nature of its symptoms. Diagnostic methods include:
- Thoracentesis: Analysis of pleural fluid can reveal low pH and low glucose levels, with a high creatinine concentration compared to serum levels.
- Imaging studies: CT scan and ultrasound can help identify the source of urine leakage and any associated renal abnormalities.

Treatment
The primary treatment for urinothorax involves addressing the underlying cause of urine leakage. This may include:
- Surgical repair of any urinary tract injuries.
- Placement of a nephrostomy tube to divert urine flow and relieve pressure.
- Antibiotics if infection is present.

Prognosis
The prognosis for patients with urinothorax is generally good if the underlying cause is identified and treated promptly. Delayed treatment can lead to complications such as infection or respiratory distress.
Related pages
References
- Light, R. W. (2002). "Pleural Diseases." Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Porcel, J. M., & Light, R. W. (2006). "Pleural effusions." Dis Mon, 52(2), 29-86.

-
Pleural effusion caused by urinothorax
-
CT scan showing placement of the nephrostomy tube in a case of urinothorax being treated
-
Urinothorax