Causal graph: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Category:Epidemiology]] | [[Category:Epidemiology]] | ||
[[Category:Machine learning]] | [[Category:Machine learning]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:College_notID.png|Causal graph without ID | |||
File:College_notID_proj.png|Projected causal graph without ID | |||
File:College.png|Causal graph | |||
File:College_proj.png|Projected causal graph | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:22, 18 February 2025
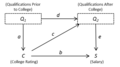
Causal graph is a directed graph that is used to visually represent and analyze the causes of a particular event or state. The nodes in the graph represent variables, and the edges represent causal relationships between the variables.
Definition[edit]
A causal graph, also known as a causal diagram or a causal model, is a graphical model that encodes causal relationships among variables of interest. These graphs are used in various fields such as statistics, epidemiology, and machine learning to understand and predict the effects of interventions, to plan studies and experiments, and to derive statistical estimation algorithms.
Structure[edit]
The structure of a causal graph consists of nodes and edges. The nodes represent variables, and the edges represent causal relationships between the variables. An edge from node A to node B indicates that A has a direct causal effect on B. The absence of an edge between two nodes indicates that there is no direct causal relationship between the variables they represent.
Uses[edit]
Causal graphs are used in a variety of fields for different purposes. In statistics, they are used to understand and predict the effects of interventions. In epidemiology, they are used to plan studies and experiments. In machine learning, they are used to derive statistical estimation algorithms.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />