Injection (medicine): Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Drawing-syringes-with-needle.jpg|Drawing of syringes with needle | |||
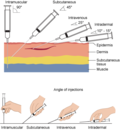
File:Needle-insertion-angles-1_(edited).png|Needle insertion angles | |||
File:Mantoux_tuberculin_skin_test.jpg|Mantoux tuberculin skin test | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:08, 18 February 2025
Injection (medicine)
An injection is a method of delivering drugs or vaccines directly into a patient's body using a needle and syringe. This method bypasses the digestive system, allowing for immediate absorption of the substance into the bloodstream.
Types of injections[edit]
There are several types of injections, each targeting a different layer of the skin or tissue. These include:
- Intradermal injection: This type of injection is administered into the dermis, or the outermost layer of skin.
- Subcutaneous injection: This injection is given into the fatty layer of tissue just beneath the skin.
- Intramuscular injection: This injection is delivered into a muscle, allowing for faster absorption into the bloodstream.
- Intravenous injection: This injection is administered directly into a vein, providing immediate delivery of the substance into the bloodstream.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure for administering an injection varies depending on the type of injection and the specific medication being delivered. However, the general steps include:
- Preparing the injection site with an antiseptic to prevent infection.
- Inserting the needle at the correct angle and depth for the type of injection.
- Delivering the medication by slowly pushing the plunger of the syringe.
- Removing the needle and applying pressure to the injection site to prevent bleeding.
Risks and complications[edit]
While injections are generally safe, they can sometimes lead to complications such as:
- Pain at the injection site
- Infection
- Allergic reaction
- Bleeding or bruising
- Nerve damage
Patients should always consult with their healthcare provider before receiving an injection to discuss potential risks and benefits.
See also[edit]
-
Drawing of syringes with needle
-
Needle insertion angles
-
Mantoux tuberculin skin test