Translational glycobiology: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Biotechnology]] | [[Category:Biotechnology]] | ||
[[Category:Medical research]] | [[Category:Medical research]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glycosylation.jpg|Translational glycobiology | |||
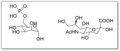
File:Different_Constituents_of_Protein_Glycans.tif|Different constituents of protein glycans | |||
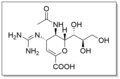
File:Zanamivir_Structure.tif|Zanamivir structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:00, 18 February 2025
Study of the role of glycans in biological processes
Translational glycobiology is a field of study that focuses on the application of glycobiology to develop new therapeutic and diagnostic tools. It involves understanding the structure and function of glycans, which are complex carbohydrates that play critical roles in various biological processes.
Overview[edit]
Translational glycobiology bridges the gap between basic glycobiology research and clinical applications. It aims to translate discoveries in glycan biology into practical solutions for health and disease management. Glycans are involved in numerous cellular functions, including cell-cell communication, immune response, and pathogen recognition.
Glycosylation[edit]

Glycosylation is the enzymatic process that attaches glycans to proteins, lipids, or other organic molecules. This modification is crucial for the stability and function of many proteins. Glycosylation affects protein folding, distribution, and activity, and is essential for proper cellular function.
Applications[edit]
Translational glycobiology has several applications in medicine and biotechnology:
- Cancer therapy: Aberrant glycosylation patterns are often associated with cancer. Understanding these patterns can lead to the development of glycan-based biomarkers for early cancer detection and targeted therapies.
- Infectious diseases: Glycans on the surface of pathogens can be targeted to develop vaccines and antiviral drugs. For example, the structure of viral glycoproteins can be analyzed to design inhibitors that block viral entry into host cells.
- Autoimmune diseases: Glycans play a role in immune system regulation. Modulating glycan interactions can help in designing therapies for autoimmune conditions.
Research Techniques[edit]
Translational glycobiology employs various techniques to study glycans and their functions:
- Mass spectrometry: Used to analyze glycan structures and compositions.
- Glycan microarrays: Allow high-throughput screening of glycan interactions with proteins or cells.
- X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy: Provide detailed structural information about glycan-protein complexes.
Challenges[edit]
The complexity and diversity of glycan structures pose significant challenges in translational glycobiology. Unlike nucleic acids and proteins, glycans are not directly encoded by the genome, making their study more complex. Additionally, the lack of standardized methods for glycan analysis hinders progress in the field.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Translational glycobiology
-
Different constituents of protein glycans
-
Zanamivir structure