Embryonal carcinoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
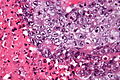
File:Embryonal_carcinoma_-_very_high_mag_-_cropped.jpg|Embryonal carcinoma - very high magnification | |||
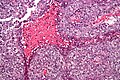
File:Embryonal_carcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg|Embryonal carcinoma - high magnification | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 02:00, 18 February 2025
Embryonal carcinoma is a rare form of cancer that originates in the germ cells, which are cells that can develop into any type of cell in the body. This type of cancer is most commonly found in the testicles, but can also occur in other parts of the body, such as the ovaries, brain, lungs, or liver.
Symptoms
The symptoms of embryonal carcinoma can vary depending on the location of the tumor. In the testicles, symptoms may include a lump or swelling, pain, or a feeling of heaviness. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, symptoms may include abdominal pain, back pain, cough, shortness of breath, or headaches.
Causes
The exact cause of embryonal carcinoma is not known. However, it is believed to be related to abnormalities in the germ cells. Certain factors may increase the risk of developing this type of cancer, including a history of undescended testicles, Klinefelter syndrome, or previous treatment for testicular cancer.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of embryonal carcinoma typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. A biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for embryonal carcinoma may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and the patient's preferences.
Prognosis
The prognosis for embryonal carcinoma varies depending on the stage of the cancer and the patient's overall health. With early detection and treatment, the prognosis can be good.