Dimethyl dicarbonate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
{{food-stub}} | {{food-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
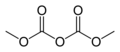
File:Dimethyl-dicarbonate-2D-skeletal.png|Dimethyl dicarbonate 2D skeletal structure | |||
File:Dimethyl-dicarbonate-3D-balls.png|Dimethyl dicarbonate 3D ball-and-stick model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:32, 18 February 2025
Dimethyl dicarbonate (DMDC) is a liquid chemical compound used in the food industry as a preservative. It is colorless, odorless, and is often used in beverages such as wine, carbonated drinks, and fruit juices to inhibit the growth of yeast, bacteria, and mold.
Chemical Properties[edit]
DMDC is a carbonate ester derived from carbonic acid and methanol. It has the chemical formula C4H6O5 and a molecular weight of 134.09 g/mol. It is soluble in water and most organic solvents.
Uses[edit]
DMDC is primarily used as a microbial control agent in non-alcoholic beverages. It works by penetrating the cell membrane of microorganisms and inactivating their enzymes, thereby preventing them from reproducing. DMDC is also used in the wine industry to prevent secondary fermentation and spoilage.
Safety[edit]
DMDC is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, it can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract if not handled properly.
Regulation[edit]
In the United States, the use of DMDC is regulated by the FDA. The maximum allowable concentration in beverages is 200 parts per million (ppm). In the European Union, the use of DMDC is regulated by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which has set a maximum allowable concentration of 250 ppm.
See Also[edit]
-
Dimethyl dicarbonate 2D skeletal structure
-
Dimethyl dicarbonate 3D ball-and-stick model