Dimethylheptylpyran: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
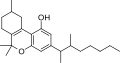
File:Dimethylheptylpyran.svg|Dimethylheptylpyran | |||
File:Dibenzopyran_and_monoterpenoid_numbering_of_tetrahydrocannabinol.svg|Dibenzopyran and monoterpenoid numbering of tetrahydrocannabinol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:19, 18 February 2025
Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP) is a synthetic analogue of THC, a compound found in cannabis. It was first synthesized in the 1940s by the American chemist, Roger Adams, and his team at the University of Illinois.
History[edit]
DMHP was developed as part of a research project by the United States military during the 1960s. The aim of the project was to create a non-lethal incapacitating agent. The compound was given the code name EA 2233 and was one of the most potent compounds tested.
Chemistry[edit]
DMHP is a derivative of THC, the main active ingredient in cannabis. It is a complex molecule with a seven-carbon side chain, making it 30 times more potent than THC. The compound is also known as 3-(1,2-dimethylheptyl)-6a,7,10,10a-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-6,6-dimethyl-6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-9-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Effects[edit]
The effects of DMHP are similar to those of THC but are much more potent and long-lasting. The compound has a half-life of 20-48 hours, compared to the 2-3 hours of THC. The effects include euphoria, altered perception, and severe sedation.
Legal status[edit]
DMHP is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States, meaning it has a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use.