Excimer: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
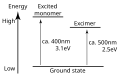
File:Excimer_energy_diagram.svg|Excimer energy diagram | |||
File:Molecule_HOMO-LUMO_diagram.svg|Molecule HOMO-LUMO diagram | |||
File:Arenephotocycloadditions.svg|Arene photocycloadditions | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:14, 18 February 2025
Excimer is a term used in Chemistry to describe a type of molecule that is formed from the combination of two, or more, identical molecules in an excited state. The term "excimer" is derived from the words "excited" and "dimer". Excimers are often formed when a photon is absorbed into a molecule, causing it to become excited and to bind with another molecule in its ground state.
Excimers are typically unstable and have a short lifespan. They will quickly return to their ground state, releasing a photon in the process. This release of energy is often in the form of ultraviolet light, which is why excimers are commonly used in laser technology.
Excimer Lasers[edit]
Excimer lasers are a type of gas laser that is powered by an electric discharge. They are used in a variety of applications, including laser eye surgery, microelectronics manufacturing, and laser spectroscopy.
Excimer lasers work by using a mixture of a noble gas and a reactive gas. When the gas mixture is excited by an electric discharge, it forms an excimer, which then decays to its ground state and releases a photon. This photon is then amplified to produce a powerful laser beam.
Applications[edit]
Excimer lasers have a wide range of applications. They are used in laser eye surgery to reshape the cornea and correct vision problems such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
In the field of microelectronics, excimer lasers are used in lithography to create patterns on semiconductor wafers. They are also used in laser spectroscopy to study the properties of molecules.