Acetamiprid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
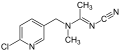
File:Acetamiprid_Structural_Formulae_V.1.svg|Structural formula of acetamiprid | File:Acetamiprid_Structural_Formulae_V.1.svg|Structural formula of acetamiprid | ||
File:Acetamiprid_3D_ball.png|3D ball model of acetamiprid | File:Acetamiprid_3D_ball.png|3D ball model of acetamiprid | ||
</gallery> | |||
== Acetamiprid == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Acetamiprid_Structural_Formulae_V.1.svg|Structural formula of Acetamiprid | |||
File:Acetamiprid_3D_ball.png|3D ball model of Acetamiprid | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:01, 18 February 2025
A neonicotinoid insecticide
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Acetamiprid is a neonicotinoid insecticide that is used to control a variety of insect pests. It is particularly effective against aphids, whiteflies, and thrips. Acetamiprid is known for its systemic action, which allows it to be absorbed by plants and transported throughout their tissues, providing protection against pests that feed on the plant.
Chemical properties[edit]
Acetamiprid is a member of the neonicotinoid class of insecticides, which are chemically similar to nicotine. The chemical structure of acetamiprid includes a chloropyridinyl group and an acetamidine group, which contribute to its insecticidal activity. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and organic solvents.
Mode of action[edit]
Acetamiprid acts on the nervous system of insects by binding to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. This binding leads to the disruption of nerve signal transmission, causing paralysis and eventually death of the insect. The specificity of acetamiprid for insect receptors over mammalian receptors contributes to its safety profile for humans and other non-target organisms.
Uses[edit]
Acetamiprid is used in agriculture to protect crops such as cotton, vegetables, fruit trees, and ornamental plants from insect damage. It is applied as a foliar spray or soil treatment and is effective at low application rates. Its systemic properties make it particularly useful for controlling sucking insects that are difficult to reach with contact insecticides.
Environmental impact[edit]
As a neonicotinoid, acetamiprid has been scrutinized for its potential impact on pollinators, particularly bees. While it is considered less toxic to bees than some other neonicotinoids, there is ongoing research into its effects on bee populations and other beneficial insects. Acetamiprid is also subject to environmental regulations to minimize its impact on non-target species and ecosystems.
Safety[edit]
Acetamiprid is classified as slightly toxic to humans and other mammals. It has a relatively low acute toxicity, but exposure should still be minimized to prevent potential health effects. Personal protective equipment is recommended for individuals handling the chemical.
Related pages[edit]
-
Structural formula of acetamiprid
-
3D ball model of acetamiprid
Acetamiprid[edit]
-
Structural formula of Acetamiprid
-
3D ball model of Acetamiprid