Chiral derivatizing agent: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:R-MTPA.png | |||
File:Amide_on_silica.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:56, 17 February 2025
Chiral derivatizing agents (CDAs) are chemical compounds used in the analysis of chiral molecules. They play a crucial role in the field of chiral chromatography and NMR spectroscopy by enabling the differentiation between enantiomers of a chiral compound. These agents react with chiral substances to form diastereomers, which are distinguishable by their physical and chemical properties, facilitating the separation and identification of the enantiomers.
Overview[edit]
Chiral derivatizing agents are essential tools in analytical chemistry, especially in the pharmaceutical industry, where the chirality of a drug can affect its efficacy and safety. By forming diastereomers with different enantiomers, CDAs allow for the separation of these enantiomers using conventional analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography (GC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Mechanism[edit]
The mechanism of action of chiral derivatizing agents involves the formation of covalent bonds between the CDA and the chiral molecule. This reaction results in the creation of diastereomers, which are not mirror images of each other and therefore have different physical and chemical properties. These differences allow for the separation of the diastereomers using analytical techniques.
Types of Chiral Derivatizing Agents[edit]
Chiral derivatizing agents can be broadly classified based on their application in different analytical techniques:
For NMR Spectroscopy[edit]
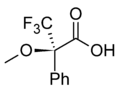
In NMR spectroscopy, CDAs are used to induce shifts in the NMR signals of enantiomers, making it possible to distinguish between them. Examples include MOSHER'S ACID and its derivatives, which are widely used in the determination of enantiomeric purity and configuration.
For Chromatography[edit]
In chromatography, CDAs are used to modify chiral compounds, making them amenable to separation by GC or HPLC. Examples include derivatizing agents like (S)-Naproxen and (R)-Phenylethylamine, which are used to separate amino acids and other chiral compounds.
Applications[edit]
Chiral derivatizing agents find applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceutical analysis, where they are used to determine the enantiomeric purity of drugs.
- Biochemical research, for the study of biomolecules and their chiral properties.
- Environmental chemistry, in the analysis of chiral pollutants.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit]
While chiral derivatizing agents have significantly advanced the analysis of chiral molecules, there are challenges, such as the need for high-purity CDAs and the development of universal CDAs that can react with a wide range of chiral molecules. Ongoing research focuses on overcoming these challenges and improving the efficiency and applicability of CDAs in chiral analysis.
See Also[edit]