Picrotoxin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
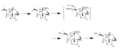
File:Picrotoxinin_Synthesis.png|Picrotoxinin Synthesis | |||
File:Picrotin_Synthesis.png|Picrotin Synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 17 February 2025
Picrotoxin, also known as cocculin, is a poisonous crystalline plant compound. It was first isolated by the French chemists Pierre François Guillaume Boullay (1777–1869) and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou (1795–1877) in 1812. The name "picrotoxin" is derived from the Greek words "picros" (bitter) and "toxicon" (poison).
Etymology[edit]
The term "picrotoxin" is a compound of two Greek words: "picros", meaning bitter, and "toxicon", meaning poison. This name was given due to the bitter taste and toxic properties of the compound.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Picrotoxin is a complex of two similar chemical compounds: picrotoxinin and picrotin. Picrotoxinin is the most toxic and active component. The chemical formula of picrotoxinin is C15H16O6, and for picrotin it is C15H18O7.
Source[edit]
Picrotoxin is obtained from the fruit of the plant Anamirta cocculus, commonly known as the Cocculus indicus or fish berry. This plant is native to India and other parts of Southeast Asia.
Pharmacology[edit]
Picrotoxin acts as a non-competitive antagonist at GABA_A receptor, a type of ionotropic receptor. It binds to the chloride ion channel pore of this receptor and blocks the action of GABA, a neurotransmitter that normally induces a calming effect in the brain. This blocking action leads to an increase in the excitability of the central nervous system.
Medical Use[edit]
Picrotoxin is used in medicine as a central nervous system stimulant. It is also used as an antidote in barbiturate and benzodiazepine poisoning to counteract the excessive inhibitory effect of these drugs on the central nervous system.
Toxicity[edit]
Picrotoxin is a powerful poison. Ingestion can lead to symptoms such as convulsions, difficulty in breathing, and death due to respiratory failure. The lethal dose for humans is not known, but in mice, the LD50 is around 15 mg/kg.